SparkSQL架构
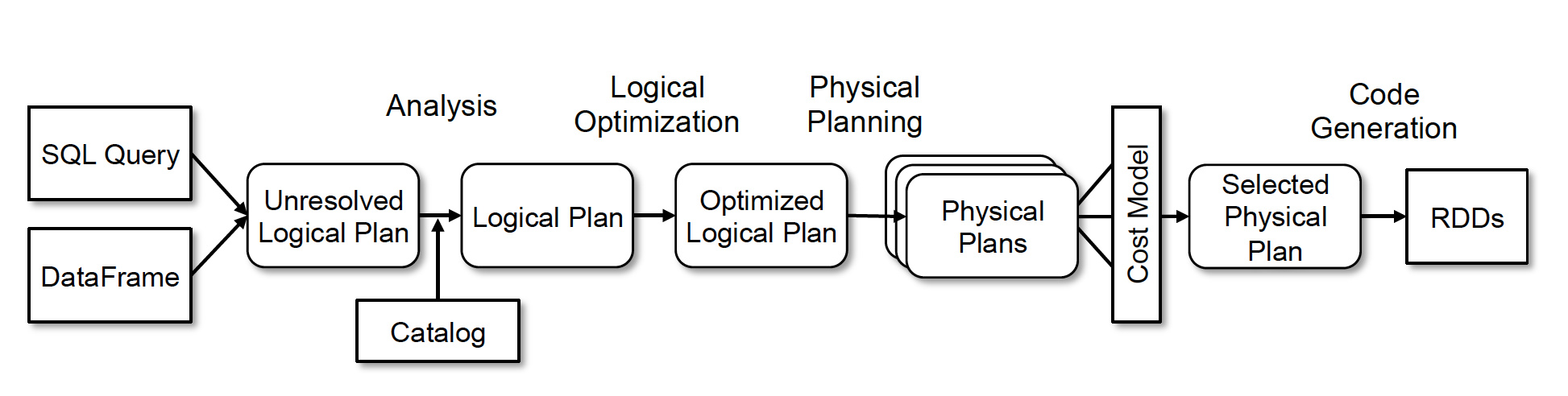
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
== Logical Plan ==
Project [t1_c1#1, t1_c2#2]
+- Filter (t1_c1#1 > 6)
+- SubqueryAlias mysql_ttt_t1
+- View (`mysql_ttt_t1`, [id#0,t1_c1#1,t1_c2#2,t1_c3#3,t1_c4#4])
+- Relation [id#0,t1_c1#1,t1_c2#2,t1_c3#3,t1_c4#4] JDBCRelation((select * from ttt.t1) SPARK_GEN_SUBQ_0) [numPartitions=1]
== Analyzed Logical Plan ==
Project [t1_c1#1, t1_c2#2]
+- Filter (t1_c1#1 > 6)
+- SubqueryAlias mysql_ttt_t1
+- View (`mysql_ttt_t1`, [id#0,t1_c1#1,t1_c2#2,t1_c3#3,t1_c4#4])
+- Relation [id#0,t1_c1#1,t1_c2#2,t1_c3#3,t1_c4#4] JDBCRelation((select * from ttt.t1) SPARK_GEN_SUBQ_0) [numPartitions=1]
== Optimized Logical Plan ==
Project [t1_c1#1, t1_c2#2]
+- Filter (isnotnull(t1_c1#1) AND (t1_c1#1 > 6))
+- Relation [id#0,t1_c1#1,t1_c2#2,t1_c3#3,t1_c4#4] JDBCRelation((select * from ttt.t1) SPARK_GEN_SUBQ_0) [numPartitions=1]
== Physical Plan ==
Scan JDBCRelation((select * from ttt.t1) SPARK_GEN_SUBQ_0) [numPartitions=1] [t1_c1#1,t1_c2#2] PushedAggregates: [], PushedFilters: [*IsNotNull(t1_c1), *GreaterThan(t1_c1,6)], PushedGroupby: [], ReadSchema: struct<t1_c1:int,t1_c2:int>
== executedPlan ==
*(1) Scan JDBCRelation((select * from ttt.t1) SPARK_GEN_SUBQ_0) [numPartitions=1] [t1_c1#1,t1_c2#2] PushedAggregates: [], PushedFilters: [*IsNotNull(t1_c1), *GreaterThan(t1_c1,6)], PushedGroupby: [], ReadSchema: struct<t1_c1:int,t1_c2:int>
SparkSQL愿景
- Write less code
- Read less data
- Let the optimizer do the hard work
Write less code
- 对不同的数据类型使用统一的接口来读写
- ETL 可以使用自定义数据源
- 常用的数据操作可以使用DataFrame的API非常简洁的完成。
- Schema inference (Schema推导) 比如半结构化的数据,如json可以自动推导字段
- Schema merging 比如int 类型字段和double类型字段合并,可以自动兼容的使用double类型。
- Partition Discovery(自动的分区探测)
Read less data
1.使用列式存储(columnar formats),比如Parquet、ORC、RCFile
2.使用分区裁剪(partitioning pruning),比如按天分区,按小时分区等
3.利用数据文件中附带的统计信息进行剪枝:例如每段数据都带有最大值、最小值和NULL值等统计信息,当某一数据段肯定不包含查询条件的目标数据时,可以直接跳过这段数据。(例如字段age某段最大值为20,但查询条件是>50岁的人时,显然可以直接跳过这段)
4.将查询源中的各种信息下推至数据源处,从而充分利用数据源自身的优化能力来完成剪枝、过滤条件下推等优化。
Let the optimizer do the hard work
Catalyst优化器对SQL语句进行优化,从而得到更有效的执行方案。
即使我们在写SQL的时候没有考虑这些优化的细节,Catalyst也可以帮我们做到不错的优化结果
Datasource API
简介
Spark Datasource API 是一套连接外部数据源和Spark引擎的框架。
它主要是给Spark框架提供一种快速读取外界数据的能力,它可以方便地把不同的数据格式通过DataSource API注册成Spark的表,然后通过Spark SQL直接读取。它可以充分利用Spark分布式的优点进行并发读取,而且SparkSQL本身有一个很好的Catalyst优化引擎,能够极大的加快任务的执行。 Spark Datasource API 同时提供了一套优化机制,如将列剪枝和过滤操作下推至数据源侧,减少数据读取数量,提高数据处理效率。
Spark DataSource API 典型的工作方式:
sparkSession //SparkSession .read .format(“csv”) //驱动类,类似JDBC的driver class .options(Map(…)) //需要额外传递给驱动类的参数 .load(“hdfs:///…”) //数据文件路径
DataSource来源
目前Spark DataSource的来源主要有三个:
- Spark 原生支持的DataSource,如常用的csv,orc,parquet;
- Spark Packages 网站中纳入的第三方包;
- 随其他项目一起发布的内嵌DataSource,如ES-Hadoop等。
DataSourceV1
- 基于 Spark 2.4.4。
读流程
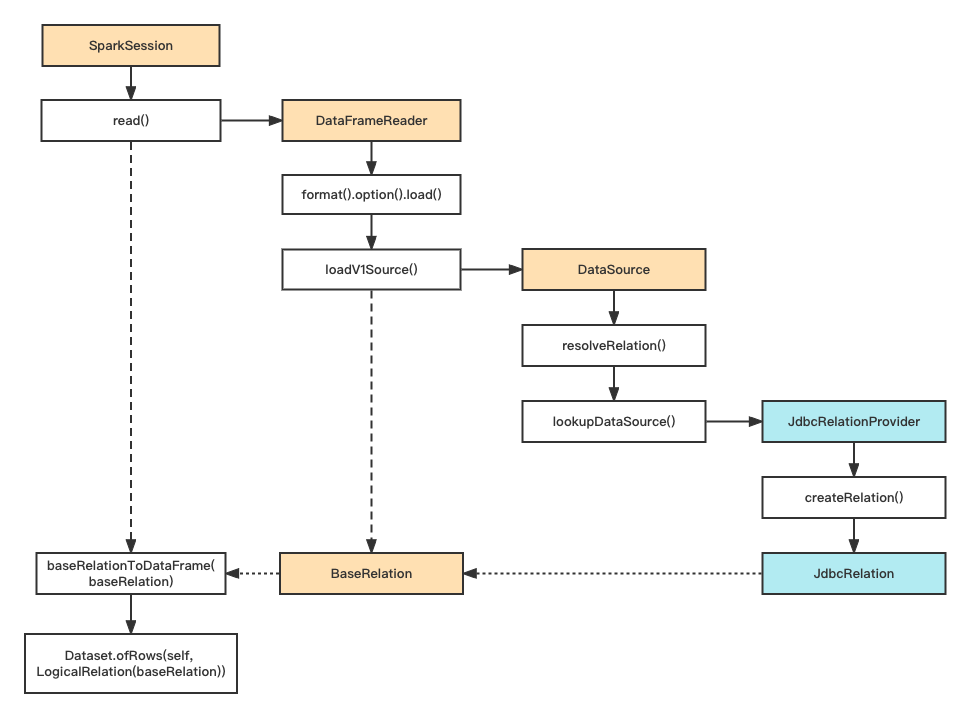
sparkSession // SparkSession
.read // DataFrameReader
.format(“csv”)
.options(Map())
.load(“path”) // DataFrame
SparkSession.read() 返回 DataFrameReader,它是 DataSource 读数据的入口。
def read: DataFrameReader = new DataFrameReader(self)
format() 方法指定数据源类型。
def format(source: String): DataFrameReader = { this.source = source this }
options()方法配置数据源相关参数。
load() 方法加载数据源实现类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
/**
* Loads input in as a `DataFrame`, for data sources that support multiple paths.
* Only works if the source is a HadoopFsRelationProvider.
*
* @since 1.6.0
*/
@scala.annotation.varargs
def load(paths: String*): DataFrame = {
if (source.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT) == DDLUtils.HIVE_PROVIDER) {
throw new AnalysisException("Hive data source can only be used with tables, you can not " +
"read files of Hive data source directly.")
}
val cls = DataSource.lookupDataSource(source, sparkSession.sessionState.conf)
// DataSourceV2
if (classOf[DataSourceV2].isAssignableFrom(cls)) {
val ds = cls.newInstance().asInstanceOf[DataSourceV2]
if (ds.isInstanceOf[ReadSupport]) {
val sessionOptions = DataSourceV2Utils.extractSessionConfigs(
ds = ds, conf = sparkSession.sessionState.conf)
val pathsOption = {
val objectMapper = new ObjectMapper()
DataSourceOptions.PATHS_KEY -> objectMapper.writeValueAsString(paths.toArray)
}
Dataset.ofRows(sparkSession, DataSourceV2Relation.create(
ds, sessionOptions ++ extraOptions.toMap + pathsOption,
userSpecifiedSchema = userSpecifiedSchema))
} else {
loadV1Source(paths: _*)
}
} else {
loadV1Source(paths: _*)
}
}
private def loadV1Source(paths: String*) = {
// Code path for data source v1.
// baseRelationToDataFrame
sparkSession.baseRelationToDataFrame(
DataSource.apply(
sparkSession,
paths = paths,
userSpecifiedSchema = userSpecifiedSchema,
className = source,
options = extraOptions.toMap)
// resolveRelation
.resolveRelation())
}
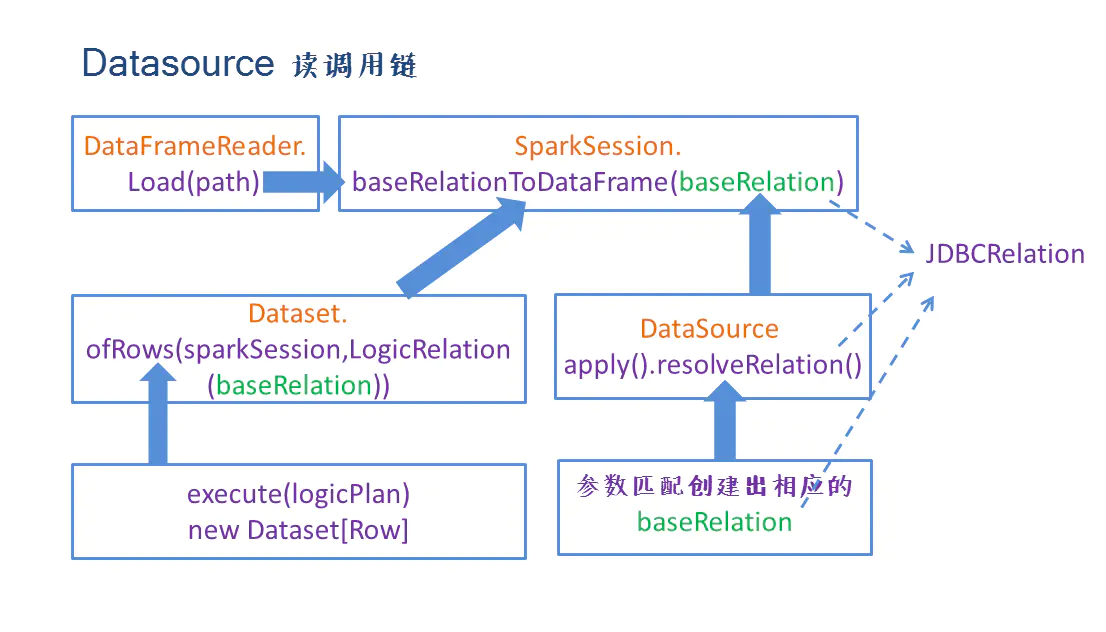
先关注loadV1Source():
- load函数最重要的功能就是将baseRelation转换成DataFrame。
- 该功能是通过sparkSession的
def baseRelationToDataFrame(baseRelation: BaseRelation): DataFrame接口实现的,其中的参数baseRelation通过DataSource类的resolveRelation方法提供。
resolveRelation()
使用反射创建出对应DataSource实例,协同用户指定的userSpecifiedSchema进行匹配,匹配成功返回对应的baseRelation:
- 如果是基于文件的,返回HadoopFsRelation实例
- 非文件的,返回如KafkaRelation或者JDBCRelation
baseRelationToDataFrame()
接受baseRelation参数返回DataFrame,是通过Dataset.ofRows(sparkSession,logicalPlan)方法实现的,其中的参数logicPlan是由LogicalRelation(baseRelation)得到。
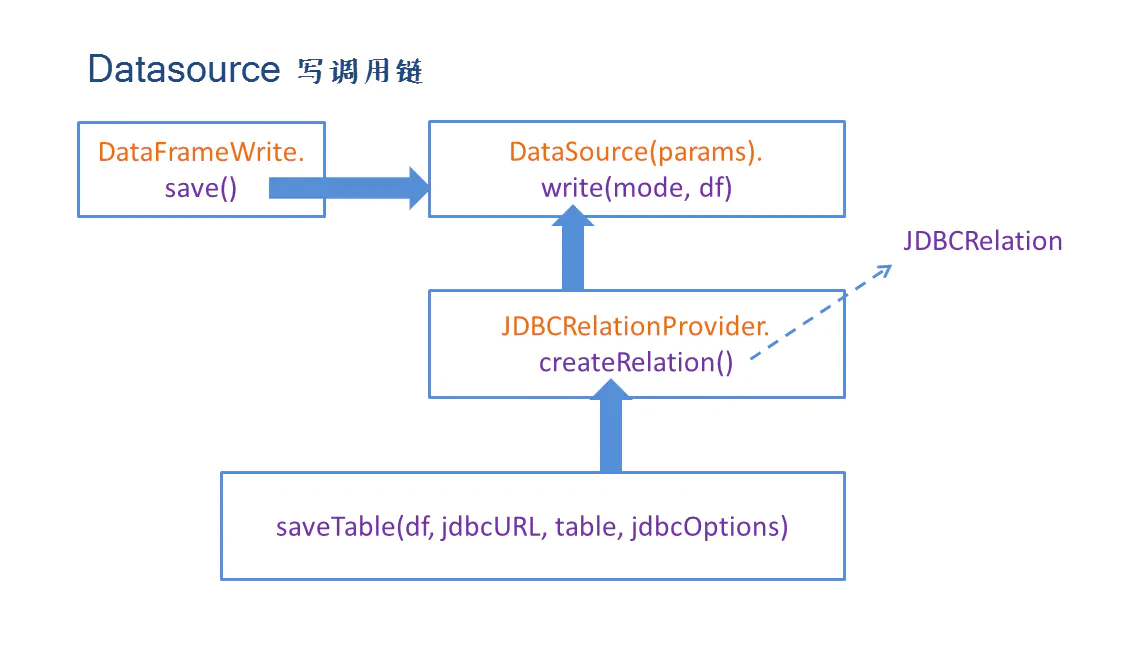
写流程
dataSet.write 返回DataFrameWriter类型对象, 它是DataSource写数据的入口。
与读机制类似,DataFrameWriter提供了DataSource的接口和参数配置方法,底层落到save方法上,运行runCommand执行写入过程,runCommand所需的LogicalPlan由对应的DataSource.planForWriting()提供。
自定义DataSource(JDBC)
所有DataSource的扩展都是基于spark\sql\core\src\main\scala\org\apache\spark\sql\sources\interfaces.scala提供的接口来实现。
一般来讲,自定义数据源需要实现以下接口和功能:
- BaseRelation:代表了一个抽象的数据源,描述了数据源和Spark SQL交互
- 数据扫描接口(根据需要实现):
- TableScan:全表数据扫描
- PrunedScan:返回指定列数据,其他的列数据源不用返回
- PrunedFilteredScan:指定列的同时,附加一些过滤条件,只返回满足过滤条件的数据
- RelationProvider: 根据用户提供的参数返回一个BaseRelation
- 数据源RDD: 将DataSource的数据读取后装配成RDD
以JDBC为例看一下DataSource扩展的流程:
JDBCRelation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
private[sql] case class JDBCRelation(
override val schema: StructType,
parts: Array[Partition],
jdbcOptions: JDBCOptions)(@transient val sparkSession: SparkSession)
extends BaseRelation
with PrunedFilteredScan
with InsertableRelation {
// ...
override def buildScan(requiredColumns: Array[String], filters: Array[Filter]): RDD[Row] = {
// Rely on a type erasure hack to pass RDD[InternalRow] back as RDD[Row]
JDBCRDD.scanTable(
sparkSession.sparkContext,
schema,
requiredColumns,
filters,
parts,
jdbcOptions).asInstanceOf[RDD[Row]]
}
override def insert(data: DataFrame, overwrite: Boolean): Unit = {
data.write
.mode(if (overwrite) SaveMode.Overwrite else SaveMode.Append)
.jdbc(jdbcOptions.url, jdbcOptions.tableOrQuery, jdbcOptions.asProperties)
}
}
JDBCRelation实现了BaseRelation、PrunedFilteredScan和InsertableRelation接口,在Spark层面描述了JDBC DataSource,以及数据读取(buildScan)和写入(insert)逻辑,它的全部工作就是重写以上三个接口的方法,方法清单:
- BaseRelation:sqlContext、schema(StructType)、sizeInBytes(预估数据量大小)、needConversion(数据类型是否需要转换)、unhandledFilters(不支持的Filter)
- PrunedFilteredScan:提供列裁剪和过滤的读取接口,只需要实现一个方法buildScan就好了,buildScan通过调用JDBCRDD.scanTable将从数据库中读出的数据装配成RDD。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
// object JDBCRDD
def scanTable(
sc: SparkContext,
schema: StructType,
requiredColumns: Array[String],
filters: Array[Filter],
parts: Array[Partition],
options: JDBCOptions): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val url = options.url
val dialect = JdbcDialects.get(url)
val quotedColumns = requiredColumns.map(colName => dialect.quoteIdentifier(colName))
// class JDBCRDD
new JDBCRDD(
sc,
JdbcUtils.createConnectionFactory(options),
pruneSchema(schema, requiredColumns),
quotedColumns,
filters,
parts,
url,
options)
}
- InsertableRelation:实现写入接口insert,将DataFrame写入DataSource,调用的是DataFrameWriter的jdbc方法。
JdbcRelationProvider
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
class JdbcRelationProvider extends CreatableRelationProvider
with RelationProvider with DataSourceRegister {
override def shortName(): String = "jdbc"
// RelationProvider
override def createRelation(
sqlContext: SQLContext,
parameters: Map[String, String]): BaseRelation = {
val jdbcOptions = new JDBCOptions(parameters)
val resolver = sqlContext.conf.resolver
val timeZoneId = sqlContext.conf.sessionLocalTimeZone
// schema
val schema = JDBCRelation.getSchema(resolver, jdbcOptions)
// 分区
val parts = JDBCRelation.columnPartition(schema, resolver, timeZoneId, jdbcOptions)
JDBCRelation(schema, parts, jdbcOptions)(sqlContext.sparkSession)
}
// CreatableRelationProvider
override def createRelation(
sqlContext: SQLContext,
mode: SaveMode,
parameters: Map[String, String],
df: DataFrame): BaseRelation = {
val options = new JdbcOptionsInWrite(parameters)
val isCaseSensitive = sqlContext.conf.caseSensitiveAnalysis
val conn = JdbcUtils.createConnectionFactory(options)()
// 判断表是否存在,如果存在判断写入模式(Overwrite、Append、ErrorIfExists、Ignore)作不同处理
....
createRelation(sqlContext, parameters)
}
}
JdbcRelationProvider实现了CreatableRelationProvider、RelationProvider、DataSourceRegister。重写了shortName和两个createRelation方法:
- DataSourceRegister:shortName方法比较简单,就是为DataSource提供一个别名,这样用户在使用实现的DataSource API的时候,提供这个别名就可以了。
- RelationProvider:重写createRelation方法,根据用户提供的参数创建baseRelation。
- CreatableRelationProvider:重写createRelation方法,基于给定的DataFrame和用户参数返回baseRelation,它描述了当数据已存在情况下的createRelation行为。支持写入模式如append、overwrite。
JDBCRDD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
private[jdbc] class JDBCRDD(
sc: SparkContext,
getConnection: () => Connection,
schema: StructType,
columns: Array[String],
filters: Array[Filter],
partitions: Array[Partition],
url: String,
options: JDBCOptions)
extends RDD[InternalRow](sc, Nil) {
override def compute(thePart: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[InternalRow] = {
// ...
// 根据filters和partition构造where条件
val myWhereClause = getWhereClause(part)
// 生成对应sql并执行
val sqlText = s"SELECT $columnList FROM ${options.table} $myWhereClause"
stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sqlText,
ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY, ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY)
stmt.setFetchSize(options.fetchSize)
rs = stmt.executeQuery()
val rowsIterator = JdbcUtils.resultSetToSparkInternalRows(rs, schema, inputMetrics)
CompletionIterator[InternalRow, Iterator[InternalRow]](
new InterruptibleIterator(context, rowsIterator), close())
}
}
一个JDBCRDD代表了关系数据库中的一张表,在Spark的Driver和Executor端都必须能够通过JDBC访问这张表,其中Driver获取schema信息,Executor获取数据。
JDBCRDD重写了RDD的getPartitions和compute方法,其中compute方法就是从关系表里读出数据,使用JdbcUtils.resultSetToSparkInternalRows( )将数据转换成SparkInternalRow格式。
JDBCRDD的伴生类中还有两个非常重要的方法:resolveTable和scanTable。这两个方法功能都比较清楚,前者是将表的schema信息以Spark 内部StructType的形式返回,后者其实是使用对应的参数创建了一个JDBCRDD的对象,对象中以RDD[InternalRow]形式映射了当前读取的关系表数据。这两个方法分别被JDBCRelation中重写的方法-schema和buildScan调用。
File Source
Spark中内置的基于文件的数据源有:text、csv、json、parquet、orc。
它们都扩展了DataSource中的FileFormat特质。
FileFormat有读、写两方面的功能:
- 读:将文件中的数据读取成为Spark内部的InternalRow格式
- 写:将Spark内部的InternalRow格式以对应的格式写入文件
该特质有几个主要的接口:
- inferSchema(自动推测模式),返回类型为
Option[StructType]: 当option中设置inferSchema为true情况下,无需用户编码显示指定模式,而是由系统自动推断模式。但是当该文件格式不支持模式推测或者传入的文件路径非法时,该方法返回None,此时需要用户显示指定schema。基本思路就是将传入的文件路径使用baseRelationToDataFrame方法转换成为DataFrame,然后取一行进行格式推测。 - prepareWrite,返回类型OutputWriterFactory: 这里通过参数spark.sql.sources.outputCommitterClass可以配置用户自定义的output committer。
- supportBatch,是否支持批量列的读入和写出
- isSplitable,单个文件是否能被切分
- buildReader,返回一个能够将单个文件读成Iterator[InternalRow]的方法
DataSource 在匹配类型时,会通过反射得到DataSource类型(FileFormat),返回HadoopFsRelation的BaseRelation,后续通过DataFrameReader的load接口获取DataFrame。
DataSourceV1缺陷
- Dependence on SQL Context and DataFrame
- Lack of Support for Columnar Read
- Lack of Partitioning and Sorting Info
- No transaction support in Write Interface
- Limited Extendability
DataSourceV2
- https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/SPARK-15689 (Batch)
- https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/SPARK-20928 (Streaming)
Spark 2.3.0
相关接口
定义DataSourceV2数据源相关接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// DataSourceV2
public interface DataSourceV2 {}
// ReadSupport
public interface ReadSupport extends DataSourceV2 {
DataSourceReader createReader(DataSourceOptions options);
}
// DataSourceReader
public interface DataSourceReader {
StructType readSchema();
List<DataReaderFactory<Row>> createDataReaderFactories();
}
// DataReaderFactory
public interface DataReaderFactory<T> extends Serializable {
default String[] preferredLocations() {
return new String[0];
}
DataReader<T> createDataReader();
}
// DataReader
public interface DataReader<T> extends Closeable {
boolean next() throws IOException;
T get();
}
PushDownOperatorsToDataSource
下推过滤到数据源:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// SupportsPushDownRequiredColumns
// 在 PushDownOperatorsToDataSource 中会调用 pruneColumns() 方法
public interface SupportsPushDownRequiredColumns extends DataSourceReader {
void pruneColumns(StructType requiredSchema);
}
// SupportsPushDownFilters
// 在 PushDownOperatorsToDataSource 中会调用 pushFilters() 方法
public interface SupportsPushDownFilters extends DataSourceReader {
Filter[] pushFilters(Filter[] filters);
Filter[] pushedFilters();
}
DataSourceV2、ReadSupport、DataSourceReader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
def load(paths: String*): DataFrame = {
if (source.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT) == DDLUtils.HIVE_PROVIDER) {
throw new AnalysisException("Hive data source can only be used with tables, you can not " +
"read files of Hive data source directly.")
}
val cls = DataSource.lookupDataSource(source, sparkSession.sessionState.conf)
// DataSourceV2
if (classOf[DataSourceV2].isAssignableFrom(cls)) {
val ds = cls.newInstance()
val options = new DataSourceOptions((extraOptions ++
DataSourceV2Utils.extractSessionConfigs(
ds = ds.asInstanceOf[DataSourceV2],
conf = sparkSession.sessionState.conf)).asJava)
// DataSourceReader
val reader = (ds, userSpecifiedSchema) match {
case (ds: ReadSupportWithSchema, Some(schema)) =>
ds.createReader(schema, options)
case (ds: ReadSupport, None) =>
ds.createReader(options)
case (ds: ReadSupportWithSchema, None) =>
throw new AnalysisException(s"A schema needs to be specified when using $ds.")
case (ds: ReadSupport, Some(schema)) =>
val reader = ds.createReader(options)
if (reader.readSchema() != schema) {
throw new AnalysisException(s"$ds does not allow user-specified schemas.")
}
reader
case _ => null // fall back to v1
}
if (reader == null) {
loadV1Source(paths: _*)
} else {
// reader -> DataSourceV2Relation -> Dataset
Dataset.ofRows(sparkSession, DataSourceV2Relation(reader))
}
} else {
loadV1Source(paths: _*)
}
}
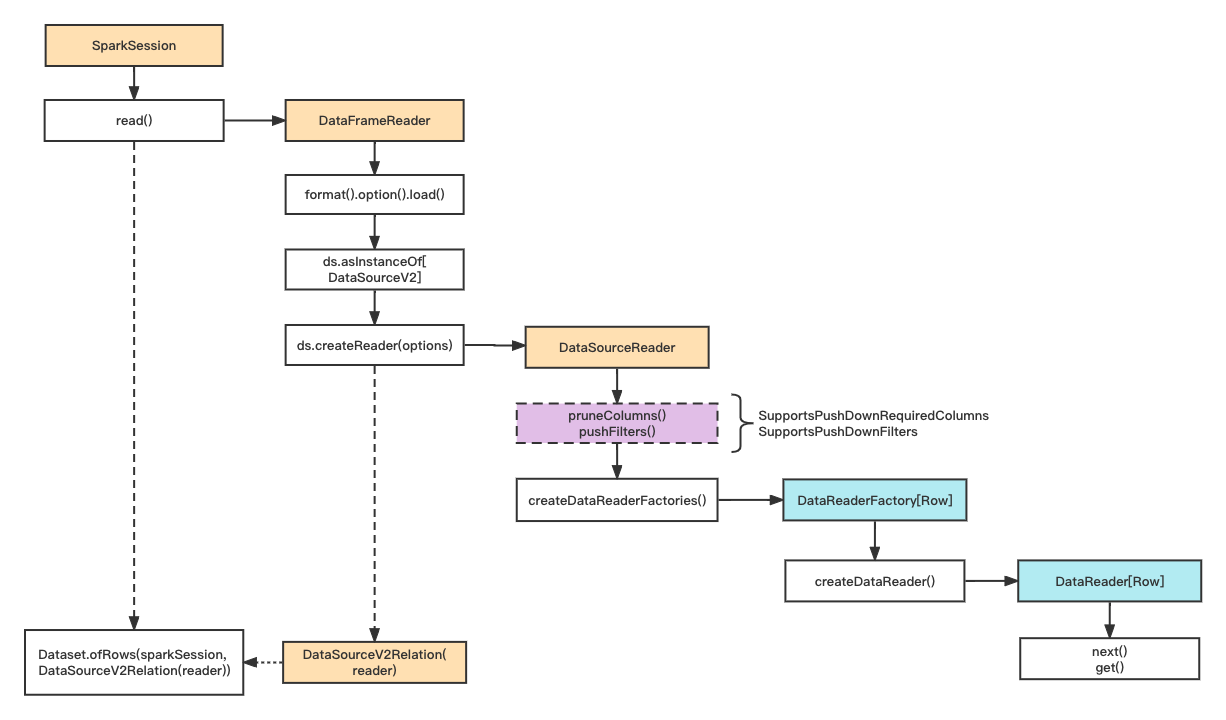
在 DataFrameReader.load() 中: reader -> DataSourceV2Relation -> Dataset
1
2
3
// DataSourceV2Relation apply():
// readSchema()
new DataSourceV2Relation(reader.readSchema().toAttributes, reader)
SparkPlanner生成物理计划,DataSourceV2Strategy:
DataSourceV2Relation -> DataSourceV2ScanExec
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
object DataSourceV2Strategy extends Strategy {
override def apply(plan: LogicalPlan): Seq[SparkPlan] = plan match {
case DataSourceV2Relation(output, reader) =>
DataSourceV2ScanExec(output, reader) :: Nil
case WriteToDataSourceV2(writer, query) =>
WriteToDataSourceV2Exec(writer, planLater(query)) :: Nil
case _ => Nil
}
}
DataReaderFactory
DataSourceV2ScanExec:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// createDataReaderFactories() -> DataReaderFactory
private lazy val readerFactories: java.util.List[DataReaderFactory[UnsafeRow]] = reader match {
case r: SupportsScanUnsafeRow => r.createUnsafeRowReaderFactories()
case _ =>
reader.createDataReaderFactories().asScala.map {
new RowToUnsafeRowDataReaderFactory(_, reader.readSchema()): DataReaderFactory[UnsafeRow]
}.asJava
}
// inputRDD
new DataSourceRDD(sparkContext, readerFactories).asInstanceOf[RDD[InternalRow]]
DataSourceRDD、DataReader
DataSourceRDD的具体计算,Iterator调用DataReader next()和get()方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = {
val reader = split.asInstanceOf[DataSourceRDDPartition[T]].readerFactory.createDataReader()
context.addTaskCompletionListener(_ => reader.close())
val iter = new Iterator[T] {
private[this] var valuePrepared = false
override def hasNext: Boolean = {
if (!valuePrepared) {
// 调用 DataReader next()
valuePrepared = reader.next()
}
valuePrepared
}
override def next(): T = {
if (!hasNext) {
throw new java.util.NoSuchElementException("End of stream")
}
valuePrepared = false
// 调用 DataReader get()
reader.get()
}
}
new InterruptibleIterator(context, iter)
}
整体流程
Spark 2.4.4
相关接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
// DataSourceV2
public interface DataSourceV2 {}
// ReadSupport
public interface ReadSupport extends DataSourceV2 {
// 新增带schema的方式,需自定义重写
default DataSourceReader createReader(StructType schema, DataSourceOptions options) {
String name;
if (this instanceof DataSourceRegister) {
name = ((DataSourceRegister) this).shortName();
} else {
name = this.getClass().getName();
}
// 默认抛出异常
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(name + " does not support user specified schema");
}
DataSourceReader createReader(DataSourceOptions options);
}
// DataSourceReader
public interface DataSourceReader {
StructType readSchema();
List<InputPartition<InternalRow>> planInputPartitions();
}
// InputPartition
public interface InputPartition<T> extends Serializable {
default String[] preferredLocations() {
return new String[0];
}
InputPartitionReader<T> createPartitionReader();
}
// InputPartitionReader
public interface InputPartitionReader<T> extends Closeable {
boolean next() throws IOException;
T get();
}
2.3 -> 2.4:
- DataReaderFactory -> InputPartition
- DataReader -> InputPartitionReader
Hive
- spark 2.4
SparkSession
SparkSession.enableHiveSupport()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
def enableHiveSupport(): Builder = synchronized {
if (hiveClassesArePresent) {
// 配置 CATALOG_IMPLEMENTATION
config(CATALOG_IMPLEMENTATION.key, "hive")
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Unable to instantiate SparkSession with Hive support because " +
"Hive classes are not found.")
}
}
sessionState:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
private val HIVE_SESSION_STATE_BUILDER_CLASS_NAME =
"org.apache.spark.sql.hive.HiveSessionStateBuilder"
private def sessionStateClassName(conf: SparkConf): String = {
// 获取 CATALOG_IMPLEMENTATION
conf.get(CATALOG_IMPLEMENTATION) match {
case "hive" => HIVE_SESSION_STATE_BUILDER_CLASS_NAME
case "in-memory" => classOf[SessionStateBuilder].getCanonicalName
}
}
@Unstable
@transient
lazy val sessionState: SessionState = {
parentSessionState
.map(_.clone(this))
.getOrElse {
// 初始化 sessionState
val state = SparkSession.instantiateSessionState(
SparkSession.sessionStateClassName(sharedState.conf),
self)
state
}
}
HiveSessionStateBuilder
包含三个重要成员:
- HiveSessionCatalog
- Analyzer
- SparkPlanner
HiveSessionCatalog
HiveSessionCatalog
org.apache.spark.sql.hive.HiveSessionCatalog继承了org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.catalog.SessionCatalog。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
private[sql] class HiveSessionCatalog(
externalCatalogBuilder: () => ExternalCatalog,
globalTempViewManagerBuilder: () => GlobalTempViewManager,
val metastoreCatalog: HiveMetastoreCatalog,
functionRegistry: FunctionRegistry,
tableFunctionRegistry: TableFunctionRegistry,
hadoopConf: Configuration,
parser: ParserInterface,
functionResourceLoader: FunctionResourceLoader)
extends SessionCatalog(
externalCatalogBuilder,
globalTempViewManagerBuilder,
functionRegistry,
tableFunctionRegistry,
hadoopConf,
parser,
functionResourceLoader) {
// ...
}
SessionCatalog
实际使用ExternalCatalog完成。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
/**
* An internal catalog that is used by a Spark Session. This internal catalog serves as a
* proxy to the underlying metastore (e.g. Hive Metastore) and it also manages temporary
* views and functions of the Spark Session that it belongs to.
*
* This class must be thread-safe.
*/
class SessionCatalog(
// ExternalCatalog: [HiveExternalCatalog, InMemoryCatalog]
externalCatalogBuilder: () => ExternalCatalog,
globalTempViewManagerBuilder: () => GlobalTempViewManager,
functionRegistry: FunctionRegistry,
tableFunctionRegistry: TableFunctionRegistry,
hadoopConf: Configuration,
parser: ParserInterface,
functionResourceLoader: FunctionResourceLoader,
cacheSize: Int = SQLConf.get.tableRelationCacheSize,
cacheTTL: Long = SQLConf.get.metadataCacheTTL) extends SQLConfHelper with Logging {
lazy val externalCatalog = externalCatalogBuilder()
def listDatabases(): Seq[String] = {
// 实际使用 ExternalCatalog
externalCatalog.listDatabases()
}
// ...
}
HiveExternalCatalog
org.apache.spark.sql.hive.HiveExternalCatalog继承了org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.catalog.ExternalCatalog。
在HiveExternalCatalog中,对数据库、数据表、数据分区和注册函数等信息的读取与操作都通过HiveClient完成。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
private[spark] class HiveExternalCatalog(conf: SparkConf, hadoopConf: Configuration)
extends ExternalCatalog with Logging{
lazy val client: HiveClient = {
HiveUtils.newClientForMetadata(conf, hadoopConf)
}
override def listDatabases(): Seq[String] = withClient {
// 实际使用 HiveClient
client.listDatabases("*")
}
// ...
}
Hive Client是用来与Hive进行交互的客户端,在Spark SQL中是定义了各种基本操作的接口,具体实现为HiveClientimpl 对象。
lookupRelation()
SessionCatalog.lookupRelation(),根据catalog生成逻辑计划节点:UnresolvedCatalogRelation 或者 View。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
def lookupRelation(name: TableIdentifier): LogicalPlan = {
synchronized {
val db = formatDatabaseName(name.database.getOrElse(currentDb))
val table = formatTableName(name.table)
// db是globalTempView的默认数据库,则为视图类型
if (db == globalTempViewManager.database) {
globalTempViewManager.get(table).map { viewDef =>
// 视图,TempView
SubqueryAlias(table, db, getTempViewPlan(viewDef))
}.getOrElse(throw new NoSuchTableException(db, table))
} else if (name.database.isDefined || !tempViews.contains(table)) {
// ExternalCatalog查询表元数据
val metadata = externalCatalog.getTable(db, table)
// 生成 Relation
getRelation(metadata)
} else {
// 视图,TempView
SubqueryAlias(table, getTempViewPlan(tempViews(table)))
}
}
}
def getRelation(
metadata: CatalogTable,
options: CaseInsensitiveStringMap = CaseInsensitiveStringMap.empty()): LogicalPlan = {
val name = metadata.identifier
val db = formatDatabaseName(name.database.getOrElse(currentDb))
val table = formatTableName(name.table)
val multiParts = Seq(CatalogManager.SESSION_CATALOG_NAME, db, table)
// 视图,生成 VIEW
if (metadata.tableType == CatalogTableType.VIEW) {
// The relation is a view, so we wrap the relation by:
// 1. Add a [[View]] operator over the relation to keep track of the view desc;
// 2. Wrap the logical plan in a [[SubqueryAlias]] which tracks the name of the view.
SubqueryAlias(multiParts, fromCatalogTable(metadata, isTempView = false))
} else {
// 物理表,生成 UnresolvedCatalogRelation
SubqueryAlias(multiParts, UnresolvedCatalogRelation(metadata, options))
}
}
private def getTempViewPlan(viewInfo: TemporaryViewRelation): View = viewInfo.plan match {
case Some(p) => View(desc = viewInfo.tableMeta, isTempView = true, child = p)
case None => fromCatalogTable(viewInfo.tableMeta, isTempView = true)
}
Analyzer
BaseSessionStateBuilder:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
protected def analyzer: Analyzer = new Analyzer(catalog, conf) {
override val extendedResolutionRules: Seq[Rule[LogicalPlan]] =
new FindDataSourceTable(session) +:
new ResolveSQLOnFile(session) +:
customResolutionRules
override val postHocResolutionRules: Seq[Rule[LogicalPlan]] =
PreprocessTableCreation(session) +:
PreprocessTableInsertion(conf) +:
DataSourceAnalysis(conf) +:
customPostHocResolutionRules
override val extendedCheckRules: Seq[LogicalPlan => Unit] =
PreWriteCheck +:
PreReadCheck +:
HiveOnlyCheck +:
customCheckRules
}
HiveSessionStateBuilder:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/**
* A logical query plan `Analyzer` with rules specific to Hive.
*/
override protected def analyzer: Analyzer = new Analyzer(catalog, conf) {
override val extendedResolutionRules: Seq[Rule[LogicalPlan]] =
// Determine the database, serde/format and schema of the Hive serde table, according to the storage properties.
new ResolveHiveSerdeTable(session) +:
// Replaces [[UnresolvedCatalogRelation]] with concrete relation logical plans.
new FindDataSourceTable(session) +:
new ResolveSQLOnFile(session) +:
customResolutionRules
override val postHocResolutionRules: Seq[Rule[LogicalPlan]] =
new DetermineTableStats(session) +:
RelationConversions(conf, catalog) +:
PreprocessTableCreation(session) +:
PreprocessTableInsertion(conf) +:
DataSourceAnalysis(conf) +:
HiveAnalysis +:
customPostHocResolutionRules
override val extendedCheckRules: Seq[LogicalPlan => Unit] =
PreWriteCheck +:
PreReadCheck +:
customCheckRules
}
不同之处在于 extendedCheckRules中少了 HiveOnlyCheck 规则,且extendedResolutionRules中多了 ResolveHiveSerdeTable 规则 ,postHocResolutionRules中多了 DetermineTableStats、RelationConversions、HiveAnalysis 规则。
-HiveOnlyCheck
在默认的Analyzer中,HiveOnlyCheck 规则会遍历逻辑算子树,如果发现 CreateTable 类型的节点且对应的 CatalogTable 是 Hive 才能够提供的,则会抛出 AnalysisException 异常,因此在Hive场景下,这条规则不再需要。
+ResolveHiveSerdeTable、RelationConversions
在 Hive 模块中,数据表统一 用 MetastoreRelation 表示,而MetastoreRelation 包含了复杂的 partition 信息 。 当 一个查询涉及的数据表不涉及分区情况时-,为了得到更优的性能,可以将 MetastoreRelation 直接转换为数据源表 ( DataSource table ) 。 具体来讲,包含两种情况。
- 读数据表,将 LogicalPlan 中所有满足条件的 MetastoreRelation 转换为 Parquet ( ORCFile) 文件格式所对应的 LogicalRelation 节点 。
- ·写数据表,即 InsertlntoTable 逻辑算子节点,同样的逻辑替换目标数据表 MetastoreRelation为对应的 LogicalRelation 节点 。 具体的实现可以参见 convertToLogicalRelation 方法。
+DetermineTableStats
统计信息。
+HiveAnalysis
一些Hive特有的转换:
- InsertIntoTable -> InsertIntoHiveTable
- CreateTable -> CreateHiveTableAsSelectCommand
- InsertIntoDir -> InsertIntoHiveDirCommand
SparkPlanner
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
/**
* Planner that takes into account Hive-specific strategies.
*/
override protected def planner: SparkPlanner = {
new SparkPlanner(session.sparkContext, conf, experimentalMethods) with HiveStrategies {
override val sparkSession: SparkSession = session
override def extraPlanningStrategies: Seq[Strategy] =
super.extraPlanningStrategies ++ customPlanningStrategies ++ Seq(HiveTableScans, Scripts)
}
}
FileSourceStrategy 生成的物理执行计划的节点为 FileSourceScanExec ,而 Hive 中则对应 HiveTableScanExec 节点 ,通过HadoopRDD读取。
Spark3 DataSourceV2
- spark 3.2
相关接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
// TableProvider
public interface TableProvider {
StructType inferSchema(CaseInsensitiveStringMap options);
default Transform[] inferPartitioning(CaseInsensitiveStringMap options) {
return new Transform[0];
}
// getTable
Table getTable(StructType schema, Transform[] partitioning, Map<String, String> properties);
default boolean supportsExternalMetadata() {
return false;
}
}
// Table
public interface Table {
String name();
StructType schema();
default Transform[] partitioning() {
return new Transform[0];
}
default Map<String, String> properties() {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
Set<TableCapability> capabilities();
}
// SupportsRead
public interface SupportsRead extends Table {
ScanBuilder newScanBuilder(CaseInsensitiveStringMap options);
}
// ScanBuilder
public interface ScanBuilder {
Scan build();
}
// Scan
public interface Scan {
StructType readSchema();
default String description() {
return this.getClass().toString();
}
default Batch toBatch() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(description() + ": Batch scan are not supported");
}
default MicroBatchStream toMicroBatchStream(String checkpointLocation) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(description() + ": Micro-batch scan are not supported");
}
default ContinuousStream toContinuousStream(String checkpointLocation) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(description() + ": Continuous scan are not supported");
}
default CustomMetric[] supportedCustomMetrics() {
return new CustomMetric[]{};
}
}
CatalogPlugin
TableProvider:
Note that, TableProvider can only apply data operations to existing tables, like read, append, delete, and overwrite. It does not support the operations that require metadata changes, like create/drop tables.
CatalogPlugin 的首要目标其实是提供一组 catalog API 用来创建、修改、加载和删除表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public interface CatalogPlugin {
void initialize(String name, CaseInsensitiveStringMap options);
String name();
default String[] defaultNamespace() {
return new String[0];
}
}
- 自定义 catalog 必须实现这个 interface
- 初始化之后会调用 CatalogPlugin 中的 initialize 方法进行初始化
- 使用 CatalogPlugin 需要添加如下配置,其中第二个配置就是我们传递给 CatalogPlugin 的 initialize 方法的参数
-
- spark.sql.catalog.catalog-name=com.example.YourCatalogClass
- spark.sql.catalog.catalog-name.(key)=(value)
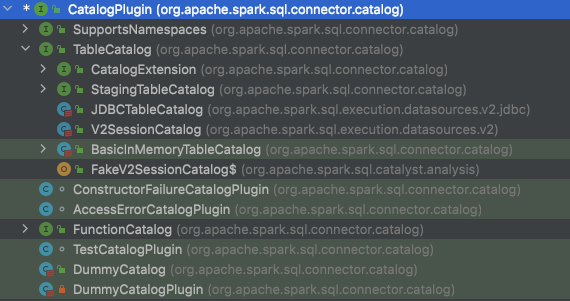
查看一下 CatalogPlugin Interface 的实现和继承关系可以看到如下图。可以看到 TableCatalog 继承了 CatalogPlugin,然后 V2SessionCatalog 和 JDBCTableCatalog 是两个具体的 class,实现了 TableCatalog。所以可以相信 TableCatalog 中实现了创建、修改、删除表的 api。
TableCatalog:
CatalogManager:
所有的 catalog 都是通过一个 Map 映射关系来管理的。
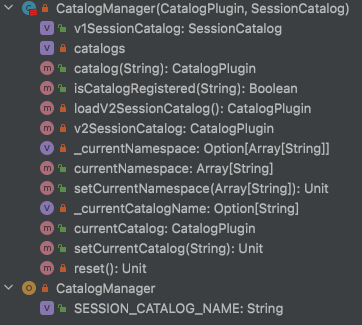
- catalogs: 一个 map: mutable.HashMap[String, CatalogPlugin],保存 catalog 名字和 Class 的隐射关系
- catalog(String):用来查找特定名字的 Catalog,返回 CatalogPlugin 接口。
使用示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
spark.conf.set("spark.sql.catalog.mysql", classOf[JDBCTableCatalog].getName)
spark.conf.set("spark.sql.catalog.mysql.url", "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/ttt?useSSL=false")
spark.conf.set("spark.sql.catalog.mysql.user", "work")
spark.conf.set("spark.sql.catalog.mysql.password", "*Work123")
val df_t1 = spark.sql("select * from mysql.ttt.t1")
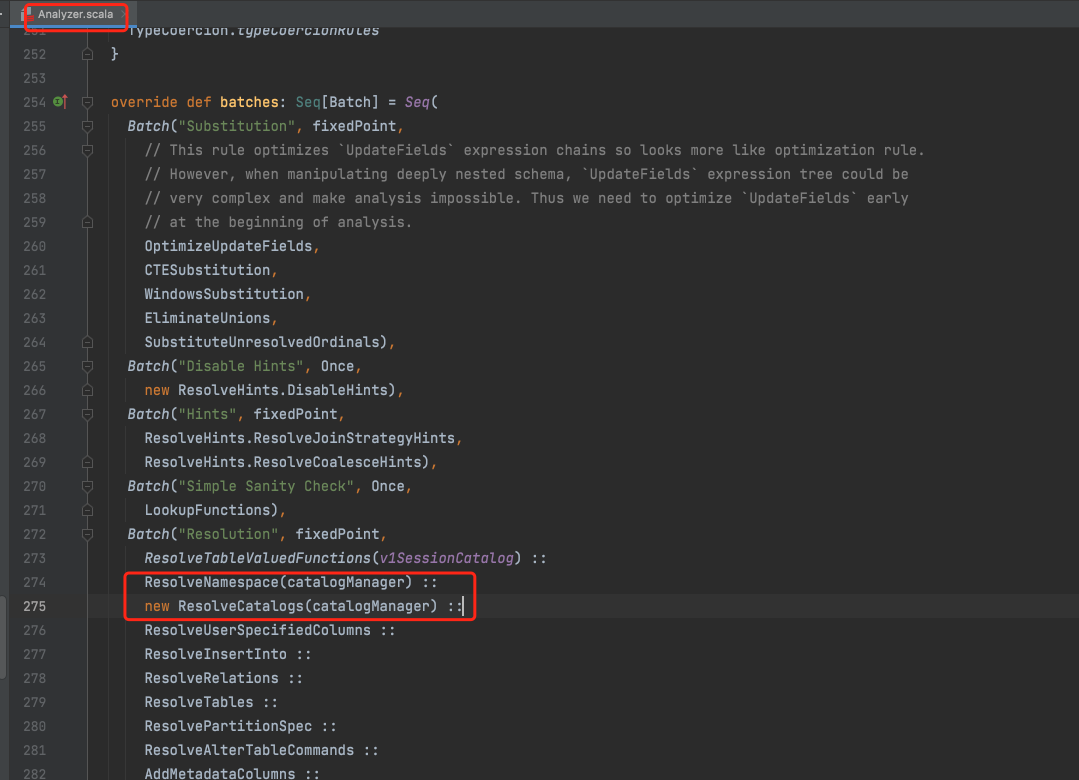
在Analyzer中进行逻辑计划分析时会调用ResolveCatalogs()规则进行解析处理。
常见数据源
| 类型 | 数据源 | 是否支持 | 实现方式 | 参考 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大数据 | Hive | 是 | enableHiveSupport()、hive.metastore.uris | |
| 大数据 | Hbase | 是 | hbase-client/SHC | https://www.jianshu.com/p/49141df754a2https://www.iteblog.com/archives/2522.htmlhttps://www.1024sou.com/article/24092.html |
| 大数据 | ClickHouse | 是 | jdbc | https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42487460/article/details/112529785 |
| 关系型数据库 | MySQL | 是 | jdbc | https://www.cnblogs.com/learn-bigdata/p/10470634.html |
| 关系型数据库 | PostgreSQL | 是 | jdbc | https://www.cnblogs.com/zhchoutai/p/8677027.html |
| 关系型数据库 | Oracle | 是 | jdbc | https://www.freesion.com/article/9933780948/ |
| 关系型数据库 | SQLServer | 是 | jdbc | https://blog.csdn.net/u013727054/article/details/105846110 |
| 关系型数据库 | Greenplum | 是 | Greenplum-Spark Connector(GSC) | https://blog.csdn.net/nazeniwaresakini/article/details/104220097https://cn.greenplum.org/greenplum-spark-connector/ |
| 关系型数据库 | Doris | 是 | jdbc/doris-spark-connector | https://ai.baidu.com/forum/topic/show/987766http://doris.incubator.apache.org/zh-CN/extending-doris/spark-doris-connector.html |
| 关系型数据库 | HANA | 是 | jdbc | https://blogs.sap.com/2016/09/09/calling-hana-views-from-apache-spark/ |
| 关系型数据库 | TiDB | 是 | tispark-assembly | https://github.com/pingcap/tispark |
| NoSQL | Redis | 是 | spark-redis | https://github.com/RedisLabs/spark-redis |
| NoSQL | MongoDB | 是 | mongo-spark | https://github.com/mongodb/mongo-spark |
| NoSQL | ElasticSearch | 是 | elasticsearch-hadoop | https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/hadoop/current/spark.html#spark-sql-readhttps://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch-hadoop |
| 实时流数据 | Kafka | 是 | spark-streaming-kafka | https://www.cnblogs.com/fnlingnzb-learner/p/13429762.html |
总结
- DataSourceAPI是SparkSQL连接其他数据源的接口。
- V1版本和V2版本差别较大。
- V2版本总的来说不稳定,spark2.3和spark2.4接口完全不一样,spark3又加了catalog。
- V2版本在spark2.3.0才支持,现有connector基本都是基于V1的。
- 后续Spark3普及了可能会更多的支持V2版本。
- 都分文件类(txt、csv、json、orc、parquet)和数据库类(JDBC)。
References
- Spark SQL的愿景
- 【Spark】DataSource API
- Madhukar’s Blog
- Spark DataSource API V2
- zhihu.com/column/Spark-BigData
- DataSourceV2 JDBC
- https://github.com/tokoko/spark-jdbc/tree/master/src/main/scala/com/tokoko/jdbc
- https://github.com/jizhang/spark-sandbox/tree/master/src/main/scala/datasource
- SparkSQL DatasourceV2 之 Multiple Catalog
- SPIP: Spark API for Table Metadata
- Spark Catalog Plugin 机制介绍