LeetCode Summary
目录
KeyPoint
难题首选动归, 受阻贪心暴力; 考虑分治思想, 配合排序哈希。
- 动态规划是解决相当数目问题的法宝;
- 滚动数组降低空间复杂度
- 贪心法并不简单;
- Dijkstra最短路径、最小生成树Prim、Kruskal算法
- 深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索,都可归结为暴力求解;
- 分支限界条件加快搜索效率
- 分治法在降低问题规模问题上很有效;
- 快速排序、归并排序 ——– 递归、广义分治法
- 排序是为了更好的查找;
- 各种排序方法的选择
- 实在不行了,空间换时间 ——– Hash
- 深入理解Hash ——– int a[65536]/int a[256]
- 有些题目需要上述两者或者多个技术综合运用。
链表
206.反转链表【简单】【链表】
反转一个单链表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class ReverseLinkedList {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode newHead = null;
while (head != null) {
// 暂存下一个节点
ListNode next = head.next;
// 讲head节点的next指向前一个节点
head.next = newHead;
// newHead更新为head
newHead = head;
// 遍历下一个节点
head = next;
}
return newHead;
}
}
92. 反转链表 II【中等】【链表】
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public class ReverseLinkedList2 {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 用cur(当前节点)和pre(前一个节点)两个进行循环反转
ListNode cur = head, pre = null;
// 先走到m反转起始位置,最后pre为m-1位置、cur为m位置节点
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 用first(m-1位置)记录反转起始位置节点,last记录反转结束位置,用于反转后连接
ListNode first = pre, last = cur;
// 反转指向需要一个额外中间节点tmp
ListNode tmp = null;
// 循环反转m到n位置节点指针
for (int i = m; i <= n; i++) {
// 记录当前节点下一个节点
tmp = cur.next;
// 当前节点下一个节点指向前一个节点
cur.next = pre;
// 前一个节点移动为当前节点
pre = cur;
// 当前节点移动到下一个节点
cur = tmp;
}
// 反转起始位置节点(m-1位置)指向pre(pre为反转后头节点,反转前原始链表第n个节点)
// 如果first为null,说明m为0,直接将pre作为head
if (first != null) {
first.next = pre;
} else {
head = pre;
}
// 反转结束位置节点指向节点cur(cur为原始链表第n+1个节点)
last.next = cur;
return head;
}
}
160.相交链表【简单】【链表】
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class IntersectionOfTwoLinkedLists {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 双指针法
ListNode pA = headA;
ListNode pB = headB;
// 当 pA 到达链表的尾部时,将它重定位到链表 B 的头结点 (你没看错,就是链表 B);
// 类似的,当 pB 到达链表的尾部时,将它重定位到链表 A 的头结点。
// 当 pA 和 pB 相遇,则 pA或pB 即为相交结点。
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA != null ? pA.next : headB;
pB = pB != null ? pB.next : headA;
}
return pA;
}
}
141.环形链表【简单】【链表、双指针】
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class LinkedListCycle {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 注意判断链表为空和一个节点链表情况
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
// 快指针
ListNode p1 = head.next;
// 慢指针
ListNode p2 = head;
// 如果快慢指针相交则存在环
while (p1 != p2) {
// 为null说明已经到链表尾部,无环
if (p1 == null || p1.next == null) {
return false;
}
p1 = p1.next.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return true;
}
}
142.环形链表 II【中等】【链表、双指针】
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
Floyd 算法:

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
public class LinkedListCycle2 {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 快指针
ListNode p1 = head;
// 慢指针
ListNode p2 = head;
// 如果快慢指针相交则存在环
do {
if (p1 == null || p1.next == null) {
return null;
}
p1 = p1.next.next;
p2 = p2.next;
} while (p1 != p2);
// 快指针从head开始
p1 = head;
while (p1 != p2) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
}
86.分隔链表【中等】【链表、双指针】
给定一个链表和一个特定值 x,对链表进行分隔,使得所有小于 x 的节点都在大于或等于 x 的节点之前。你应当保留两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class PartitionList {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
// 用两个链表分别保存小于x和大于等于x的节点;
ListNode left = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode right = new ListNode(-1);
// 用两个节点移动更新
ListNode pl = left;
ListNode pr = right;
while (head != null) {
if (head.val < x) {
pl.next = head;
pl = pl.next;
} else {
pr.next = head;
pr = pr.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
// 将右边最后一个节点的next设置为null,不然可能存在环
pr.next = null;
// 拼接左右两个链表
pl.next = right.next;
return left.next;
}
}
138.复制带随机指针的链表【中等】【哈希表、链表】
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public class CopyListWithRandomPointer {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Node tmp = head;
// 复制每个节点, A->B->C 变为 A->A'->B->B'->C->C'
while (tmp != null) {
Node newNode = new Node(tmp.val);
newNode.next = tmp.next;
tmp.next = newNode;
tmp = newNode.next;
}
// 再遍历一次,将随机指针复制到新节点
tmp = head;
while (tmp != null) {
tmp.next.random = tmp.random != null ? tmp.random.next : null;
tmp = tmp.next.next;
}
// 复制的新链表的头节点
Node headNew = head.next;
Node pOld = head;
Node pNew = head.next;
// 拆分,A->A'->B->B'->C->C' 变为两个链表 A->B->C and A'->B'->C'
while (pOld != null) {
pOld.next = pOld.next.next;
pNew.next = pNew.next != null ? pNew.next.next : null;
pOld = pOld.next;
pNew = pNew.next;
}
return headNew;
}
}
21.合并两个有序链表【简单】【链表】
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class MergeTwoSortedLists {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode res = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = res;
// 两个都不(&&)为空,比较大小添加较小节点到新链表尾部
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 拼接剩下部分
prev.next = (l1 == null) ? l2 : l1;
return res.next;
}
}
23.合并K个排序链表【困难】【堆、链表、分治算法】
合并 k 个排序链表,返回合并后的排序链表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class MergeKSortedLists {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
// 优先队列
Queue<ListNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> v1.val - v2.val);
for (ListNode node : lists) {
if (node != null) {
pq.offer(node);
}
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tail = dummyHead;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
ListNode minNode = pq.poll();
tail.next = minNode;
tail = minNode;
if (minNode.next != null) {
pq.offer(minNode.next);
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
栈、队列、堆
225.用队列实现栈【简单】【栈、设计】
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
push(x) – 元素 x 入栈; pop() – 移除栈顶元素; top() – 获取栈顶元素; empty() – 返回栈是否为空。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public class ImplementStackUsingQueues {
// 用一个队列
private LinkedList<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<>();
public ImplementStackUsingQueues() {
}
public void push(int x) {
q1.add(x);
int sz = q1.size();
// 每加入一个元素,把前面元素移动到新加入的后面
while (sz > 1) {
q1.add(q1.remove());
sz--;
}
}
public int pop() {
return q1.remove();
}
public int top() {
return q1.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty();
}
}
232.用栈实现队列【简单】【栈、设计】
使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
push(x) – 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。 pop() – 从队列首部移除元素。 peek() – 返回队列首部的元素。 empty() – 返回队列是否为空。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
public class ImplementQueueUsingStacks {
// 两个栈,新元素压入s1的栈顶,弹出时把s1元素压入s2,弹出s2的栈顶元素
private Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
// s1中压入的第一个元素(队首,栈底)
private int front;
public ImplementQueueUsingStacks() {
}
public void push(int x) {
if (s1.empty()) {
front = x;
}
s1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
// s2为空,把s1所以元素压入s2,返回s2栈顶元素
if (s2.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
// s2不为空,直接返回s2栈顶元素
return s2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
// s2不为空返回s2的栈顶元素
if (!s2.isEmpty()) {
return s2.peek();
}
// s2为空返回s1的栈底元素
return front;
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty();
}
}
155.最小栈【简单】【栈、设计】
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
push(x) —— 将元素 x 推入栈中。 pop() —— 删除栈顶的元素。 top() —— 获取栈顶元素。 getMin() —— 检索栈中的最小元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
public class MinStack {
// 数据栈
private Stack<Integer> data;
// 辅助栈,记录对应最小值
private Stack<Integer> helper;
public MinStack() {
data = new Stack<>();
helper = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
data.add(x);
// 如果辅助栈为空或者辅助栈栈顶元素大于x,压入x到栈顶
if (helper.isEmpty() || helper.peek() >= x) {
helper.add(x);
} else {
helper.add(helper.peek());
}
}
public void pop() {
// 数据栈和辅助栈同时pop
data.pop();
helper.pop();
}
public int top() {
return data.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return helper.peek();
}
}
224.基本计数器【困难】【栈、数学】
实现一个基本的计算器来计算一个简单的字符串表达式的值。
字符串表达式可以包含左括号 ( ,右括号 ),加号 + ,减号 -,非负整数和空格 ` `。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
public class BasicCalculator {
public int calculate(String s) {
int res = 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int num = 0;
// 判断正负
int sign = 1;
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (c == ' ') {
continue;
}
// 数字
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
num = num * 10 + c - '0';
}
// 如果遇到操作符,进行运算
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') {
res = res + sign * num;
sign = c == '+' ? 1 : -1;
num = 0;
}
// 遇到’(',将结果和括号前的运算保存,然后将参数重置
else if (c == '(') {
stack.push(res);
stack.push(sign);
sign = 1;
res = 0;
}
// 遇到')',计算新的结果
else if (c == ')') {
// 将')'前的运算结束
res = res + sign * num;
// 将之前的结果和操作取出来和当前结果进行运算
int signBefore = stack.pop();
int resBefore = stack.pop();
res = resBefore + signBefore * res;
sign = 1;
num = 0;
}
}
res = res + sign * num;
return res;
}
}
215.数组中的第K个最大元素【中等】【堆、分治算法】
在未排序的数组中找到第 k 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class KthLargestElementInAnArray {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
// 创建一个小顶堆(优先队列模拟)
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
for (int n : nums) {
// 堆中元素个数小于K时,新元素直接进入堆中
if (heap.size() < k) {
heap.add(n);
}
// 当堆顶小于新元素时,弹出堆顶,将新元素加入堆
else if (heap.element() < n) {
heap.poll();
heap.add(n);
}
}
return heap.poll();
}
}
295.数据流的中位数【困难】【堆、设计】
设计一个支持以下两种操作的数据结构:
void addNum(int num) - 从数据流中添加一个整数到数据结构中。 double findMedian() - 返回目前所有元素的中位数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public class FindMedianFromDataStream {
private int count;
private PriorityQueue<Integer> maxheap;
private PriorityQueue<Integer> minheap;
public FindMedianFromDataStream() {
count = 0;
maxheap = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> y - x);
minheap = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> x - y);
}
public void addNum(int num) {
count++;
maxheap.offer(num);
minheap.add(maxheap.poll());
// 如果两个堆合起来的元素个数是奇数,小顶堆要拿出堆顶元素给大顶堆
if ((count & 1) != 0) {
maxheap.add(minheap.poll());
}
}
public double findMedian() {
// 如果两个堆合起来的元素个数是偶数,数据流的中位数就是各自堆顶元素的平均值
if ((count & 1) == 0) {
return (double) (maxheap.peek() + minheap.peek()) / 2;
}
// 如果两个堆合起来的元素个数是奇数,数据流的中位数大顶堆的堆顶元素
else {
return (double) maxheap.peek();
}
}
}
贪心
455.分发饼干【简单】【贪心算法】
假设你是一位很棒的家长,想要给你的孩子们一些小饼干。但是,每个孩子最多只能给一块饼干。对每个孩子 i ,都有一个胃口值 gi ,这是能让孩子们满足胃口的饼干的最小尺寸;并且每块饼干 j ,都有一个尺寸 sj 。如果 sj >= gi ,我们可以将这个饼干 j 分配给孩子 i ,这个孩子会得到满足。你的目标是尽可能满足越多数量的孩子,并输出这个最大数值。
注意:
你可以假设胃口值为正。 一个小朋友最多只能拥有一块饼干。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class AssignCookies {
public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
int res = 0;
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < g.length && j < s.length) {
if (s[j] >= g[i]) {
res++;
i++;
}
j++;
}
return res;
}
}
376.摆动序列【中等】【贪心算法、动态规划】
如果连续数字之间的差严格地在正数和负数之间交替,则数字序列称为摆动序列。第一个差(如果存在的话)可能是正数或负数。少于两个元素的序列也是摆动序列。
例如, [1,7,4,9,2,5] 是一个摆动序列,因为差值 (6,-3,5,-7,3) 是正负交替出现的。相反, [1,4,7,2,5] 和 [1,7,4,5,5] 不是摆动序列,第一个序列是因为它的前两个差值都是正数,第二个序列是因为它的最后一个差值为零。
给定一个整数序列,返回作为摆动序列的最长子序列的长度。 通过从原始序列中删除一些(也可以不删除)元素来获得子序列,剩下的元素保持其原始顺序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class WiggleSubsequence {
public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n < 2) {
return n;
}
// 判断连续上升或者下降的波段个数
int up = 1, down = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) {
up = down + 1;
} else if (nums[i] < nums[i - 1]) {
down = up + 1;
}
}
return Math.max(up, down);
}
}
402.移掉K位数字【中等】【栈、贪心算法】
给定一个以字符串表示的非负整数 num,移除这个数中的 k 位数字,使得剩下的数字最小。
注意:
num 的长度小于 10002 且 ≥ k。 num 不会包含任何前导零。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
public class RemoveKDigits {
public String removeKdigits(String num, int k) {
LinkedList<Character> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for (char digit : num.toCharArray()) {
// 对于数字序列[d1,d2,d3,...,dn],如果d2小于d1,删除d1才能获得最小结果。
while (k > 0 && stack.size() > 0 && stack.peekLast() > digit) {
stack.removeLast();
k -= 1;
}
stack.addLast(digit);
}
// 对于单调递增序列,只需要删除末尾的数字来获得最小结果。
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
stack.removeLast();
}
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
// 去掉头部的0
boolean headZero = true;
for (char digit : stack) {
if (headZero && digit == '0') {
continue;
}
headZero = false;
res.append(digit);
}
if (res.length() == 0) {
return "0";
}
return res.toString();
}
}
55.跳跃游戏【中等】【贪心算法、数组】
给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。判断你是否能够到达最后一个位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
class JumpGame {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
// 最远可以到达的位置
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
System.out.println("i:" + i + " maxIndex:" + maxIndex);
if (i <= maxIndex) {
// 更新最远可以到达的位置
maxIndex = Math.max(maxIndex, i + nums[i]);
// 如果最远可以到达的位置大于等于数组长度,则可以到达最后一个位置
if (maxIndex >= nums.length - 1) {
return true;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
}
45.跳跃游戏2【困难】【贪心算法、数组】
给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。你的目标是使用最少的跳跃次数到达数组的最后一个位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class JumpGame2 {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
int maxPosition = 0;
int end = 0;
// 最后一个元素不需要访问
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
// 遍历i到当前maxPosition之间下一步能到的最远距离
maxPosition = Math.max(maxPosition, i + nums[i]);
if (i == end) {
end = maxPosition;
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
}
452.用最少数量的箭引爆气球【中等】【贪心算法】
在二维空间中有许多球形的气球。对于每个气球,提供的输入是水平方向上,气球直径的开始和结束坐标。由于它是水平的,所以y坐标并不重要,因此只要知道开始和结束的x坐标就足够了。开始坐标总是小于结束坐标。平面内最多存在104个气球。
一支弓箭可以沿着x轴从不同点完全垂直地射出。在坐标x处射出一支箭,若有一个气球的直径的开始和结束坐标为 xstart,xend, 且满足 xstart ≤ x ≤ xend,则该气球会被引爆。可以射出的弓箭的数量没有限制。 弓箭一旦被射出之后,可以无限地前进。我们想找到使得所有气球全部被引爆,所需的弓箭的最小数量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
class MinimumNumberOfArrowsToBurstBalloons {
public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) {
if (points.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
// 先按x_end排序
Arrays.sort(points, new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[1] - o2[1];
}
});
int res = 1;
int start, end;
// 记录当前气球的end位置
int maxPosition = points[0][1];
for (int[] p : points) {
// end位置在当前气球end位置(maxPosition)之前的所有气球都可以一次引爆
start = p[0];
end = p[1];
if (maxPosition < start) {
maxPosition = end;
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
}
871.最低加油次数【困难】【堆、动态规划】
汽车从起点出发驶向目的地,该目的地位于出发位置东面 target 英里处。沿途有加油站,每个 station[i] 代表一个加油站,它位于出发位置东面 station[i][0] 英里处,并且有 station[i][1] 升汽油。假设汽车油箱的容量是无限的,其中最初有 startFuel 升燃料。它每行驶 1 英里就会用掉 1 升汽油。当汽车到达加油站时,它可能停下来加油,将所有汽油从加油站转移到汽车中。为了到达目的地,汽车所必要的最低加油次数是多少?如果无法到达目的地,则返回 -1 。
注意:如果汽车到达加油站时剩余燃料为 0,它仍然可以在那里加油。如果汽车到达目的地时剩余燃料为 0,仍然认为它已经到达目的地。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
class MinimumNumberOfRefuelingStops {
/**
* 动态规划,时间O(N^2),空间O(N)
*/
public int minRefuelStops(int target, int startFuel, int[][] stations) {
// dp[i] 为加 i 次油能走的最远距离,需要满足 dp[i] >= target 的最小 i
int[] dp = new int[stations.length + 1];
dp[0] = startFuel;
for (int i = 0; i < stations.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j >= 0; j--) {
// 如果 dp[j] 能到达stations[i],判断更新是否加j+1次油能到更远距离
if (dp[j] >= stations[i][0]) {
dp[j + 1] = Math.max(dp[j + 1], dp[j] + stations[i][1]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) {
if (dp[i] >= target) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
递归、回溯与分治
解决一个回溯问题,实际上就是一个决策树的遍历过程。只需要思考 3 个问题:
1、路径:也就是已经做出的选择。
2、选择列表:也就是你当前可以做的选择。
3、结束条件:也就是到达决策树底层,无法再做选择的条件。
回溯算法的框架:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
result = []
def backtrack(路径, 选择列表):
if 满足结束条件:
result.add(路径)
return
for 选择 in 选择列表:
做选择
backtrack(路径, 选择列表)
撤销选择
其核心就是 for 循环里面的递归,在递归调用之前「做选择」,在递归调用之后「撤销选择」
78.求子集【中等】【位运算、数组、回溯算法】
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
观察全排列/组合/子集问题,它们比较相似,且可以使用一些通用策略解决。
首先,它们的解空间非常大:
全排列:N!;组合:N!。子集:2^N ,每个元素都可能存在或不存在。
在它们的指数级解法中,要确保生成的结果 完整 且 无冗余,有三种常用的方法:
递归
回溯
基于二进制位掩码和对应位掩码之间的映射字典生成排列/组合/子集
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
class Subsets {
/**
* 递归(遍历),时间:O(N * 2^N),空间:O(N * 2^N)
*/
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int num : nums) {
List<List<Integer>> newSubsets = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<Integer> r : res) {
newSubsets.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(r) );
}
res.addAll(newSubsets);
}
return res;
}
/**
* 回溯:时间:O(N * 2^N),空间:O(N * 2^N)
* 算法:幂集是所有长度从 0 到 n 所有子集的组合。
*/
public void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> res, int first, ArrayList<Integer> curr, int[] nums) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(curr));
for (int i = first; i < nums.length; i++) {
curr.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(res, i + 1, curr, nums);
curr.remove(curr.size() - 1);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> subsets2(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(res, 0, new ArrayList<>(), nums);
return res;
}
/**
* 位操作,字典排序(二进制排序) 子集:时间:O(N * 2^N),空间:O(N * 2^N)
* 相当于遍历,只是用位掩码来表示所有遍历
*/
public List<List<Integer>> subsets3(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int n = nums.length;
// 生成从 0..00 到 1..11 的所有 n 位掩码
for (int i = (int) Math.pow(2, n); i < (int) Math.pow(2, n + 1); i++) {
String bitmask = Integer.toBinaryString(i).substring(1);
List<Integer> curr = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (bitmask.charAt(j) == '1') {
curr.add(nums[j]);
}
}
res.add(curr);
}
return res;
}
}
90.求子集2【中等】【数组、回溯算法】
给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
class Subsets2 {
/**
* 回溯
*/
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> res, int first, ArrayList<Integer> curr, int[] nums) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(curr));
for (int i = first; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 跳过重复元素
if (i > first && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
curr.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(res, i + 1, curr, nums);
curr.remove(curr.size() - 1);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 先排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtrack(res, 0, new ArrayList<>(), nums);
return res;
}
/**
* 遍历1
* 在已有子集遍历添加当前元素时,跳过上次遍历重复元素已经添加过的子集,只添加新的部分
*/
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup2(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
res.add(new ArrayList<>());
// 新解开始位置
int start = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
List<List<Integer>> newSubsets = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < res.size(); j++) {
List<Integer> list = res.get(j);
// 跳过重复元素
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && j < start) {
continue;
}
int tmp = nums[i];
newSubsets.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list) );
}
// 更新新解开始位置
start = res.size();
res.addAll(newSubsets);
}
return res;
}
/**
* 遍历2
* 记录重复元素重复次数dupCount,在出现重复数字之前的所有解中,分别加1个重复数字, ..., dupCount个重复数字
*/
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup3(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
res.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 重复元素重复次数
int dupCount = 0;
while (((i + 1) < nums.length) && nums[i + 1] == nums[i]) {
dupCount++;
i++;
}
int tmpSize = res.size();
for (int j = 0; j < tmpSize; j++) {
List<Integer> tmpList = new ArrayList<>(res.get(j));
// 每次在上次的结果中多加 1 个重复数字
for (int k = 0; k <= dupCount; k++) {
// 加入当前重复的数字
tmpList.add(nums[i]);
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmpList));
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
40.组合总和2【中等】【数组、回溯算法】
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:
所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。 解集不能包含重复的组合。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
class CombinationSum2 {
/**
* 回溯
* 同:90.子集2
*/
public void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> res, int start, ArrayList<Integer> curr, int[] candidates, int target) {
if (target == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(curr));
} else if (target < 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
// 跳过重复元素
if (i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
curr.add(candidates[i]);
backtrack(res, i + 1, curr, candidates, target - candidates[i]);
curr.remove(curr.size() - 1);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtrack(res, 0, new ArrayList<>(), candidates, target);
return res;
}
}
22.括号生成【中等】【字符串、回溯算法】
数字 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你设计一个函数,用于能够生成所有可能的并且 有效的 括号组合。
题解2-回溯算法(深度优先遍历)+ 广度优先遍历 + 动态规划
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class GenerateParentheses {
public void backtrack(List<String> res, StringBuilder cur, int left, int right, int n) {
if (cur.length() == n * 2) {
res.add(cur.toString());
return;
}
if (left < n) {
cur.append('(');
backtrack(res, cur, left + 1, right, n);
cur.deleteCharAt(cur.length() - 1);
}
// 右括号个数一定要小于左括号个数才能再加一个右括号
if (right < left) {
cur.append(')');
backtrack(res, cur, left, right + 1, n);
cur.deleteCharAt(cur.length() - 1);
}
}
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(res, new StringBuilder(), 0, 0, n);
return res;
}
}
51.N皇后【困难】【回溯算法】
n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。给定一个整数 n,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个明确的 n 皇后问题的棋子放置方案,该方案中 ‘Q’ 和 ‘.’ 分别代表了皇后和空位。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
class NQueens {
/**
* 构造每行结果String
*/
private static List<String> charToString(char[][] array) {
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
for (char[] chars : array) {
result.add(String.valueOf(chars));
}
return result;
}
/**
* 判断是否符合要求
*/
private boolean isValid(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
// 检查列上是否已经有皇后
for (char[] chars : board) {
if (chars[col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查左上角是否有皇后
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查右下角是否有皇后
for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < board.length; i--, j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 回溯
*/
public void backtrack(List<List<String>> res, char[][] board, int row) {
if (row == board.length) {
res.add(charToString(board));
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < board.length; col++) {
if (!isValid(board, row, col)) {
continue;
}
board[row][col] = 'Q';
backtrack(res, board, row + 1);
board[row][col] = '.';
}
}
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (n <= 0) {
return null;
}
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
for (char[] chars : board) {
Arrays.fill(chars, '.');
}
backtrack(res, board, 0);
return res;
}
}
315.计算右侧小于当前元素的个数【困难】【排序、树状数组、线段树、二分查找、分治算法】
给定一个整数数组 nums,按要求返回一个新数组 counts。数组 counts 有该性质: counts[i] 的值是 nums[i] 右侧小于 nums[i] 的元素的数量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
class CountOfSmallerNumbersAfterSelf {
private int[] temp;
// 计数数组
private int[] counter;
// 索引数组
private int[] indexes;
public List<Integer> countSmaller(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int len = nums.length;
if (len == 0) {
return res;
}
temp = new int[len];
counter = new int[len];
indexes = new int[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
indexes[i] = i;
}
divide(nums, 0, len - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
res.add(counter[i]);
}
return res;
}
private void divide(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) {
return;
}
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
divide(nums, l, mid);
divide(nums, mid + 1, r);
// 归并排序的优化,如果索引数组有序,就没有必要再继续计算了
if (nums[indexes[mid]] > nums[indexes[mid + 1]]) {
merge(nums, l, mid, r);
}
}
private void merge(int[] nums, int left, int mid, int right) {
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
temp[i] = indexes[i];
}
int i = left, j = mid + 1;
for (int k = left; k <= right; k++) {
if (i > mid) {
indexes[k] = temp[j++];
} else if (j > right) {
indexes[k] = temp[i++];
// 此时 j 用完了,之前的数就和后面的区间长度构成逆序
counter[indexes[k]] += (right - mid);
} else if (nums[temp[i]] <= nums[temp[j]]) {
indexes[k] = temp[i++];
counter[indexes[k]] += (j - mid - 1);
} else {
// nums[indexes[i]] > nums[indexes[j]] 构成逆序
indexes[k] = temp[j++];
}
}
}
}
二叉树与图
113.路径之和2【中等】【树、深度优先搜索】
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
class PathSum2 {
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 用Deque双端队列比用LinkedList快十倍以上?
dfs(root, sum, new ArrayDeque<>(), res);
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int sum, Deque<Integer> tmp, List<List<Integer>> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
tmp.addLast(root.val);
if (root.val == sum && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
res.add(new LinkedList<>(tmp));
}
dfs(root.left, sum - root.val, tmp, res);
dfs(root.right, sum - root.val, tmp, res);
tmp.removeLast();
}
}
236.二叉树的最近公共祖先【中等】【树】
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class LowestCommonAncestorOfABinaryTree {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
// 如果当前结点 root 等于 NULL,则直接返回 NULL
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// 如果 root 等于 p 或者 q ,那返回 p 或者 q
if (root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
// 递归左右子树,因为是递归,使用函数后可认为左右子树已经算出结果
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
// 此时若left为空,那最终结果只要看 right
if (left == null) {
return right;
}
// 若 right 为空,那最终结果只要看 left
if (right == null) {
return left;
}
// 如果 left 和 right 都非空,root 是他们的最近公共祖先
return root;
}
}
114.二叉树展开为链表【中等】【树、深度优先搜索】
给定一个二叉树,原地将它展开为一个单链表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
class FlattenBinaryTreeToLinkedList {
TreeNode tmp = null;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
flatten(root.right);
flatten(root.left);
root.right = tmp;
root.left = null;
tmp = root;
}
}
199.二叉树的右视图【中等】【树、深度优先搜索、宽度优先搜索】
给定一棵二叉树,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
class BinaryTreeRightSideView {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) {
// 当前层节点
Deque<TreeNode> deque1 = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 下一层节点
Deque<TreeNode> deque2 = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque1.addLast(root);
bfs(deque1, deque2, res);
}
return res;
}
public void bfs(Deque<TreeNode> deque1, Deque<TreeNode> deque2, List<Integer> res) {
if (deque1.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 当前层的最后一个节点就是该层右视图节点
res.add(deque1.getLast().val);
// 遍历得到下一层节点
while (!deque1.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode tmp = deque1.removeFirst();
if (tmp.left != null) {
deque2.addLast(tmp.left);
}
if (tmp.right != null) {
deque2.addLast(tmp.right);
}
}
// 递归下下一层
bfs(deque2, deque1, res);
}
}
207.课程表【中等】【深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索、图、拓扑排序】
你这个学期必须选修 numCourse 门课程,记为 0 到 numCourse-1 。在选修某些课程之前需要一些先修课程。 例如,想要学习课程 0 ,你需要先完成课程 1 ,我们用一个匹配来表示他们:[0,1],给定课程总量以及它们的先决条件,请你判断是否可能完成所有课程的学习?
题解1-课程表(拓扑排序:入度表BFS法 / DFS法,清晰图解)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
{
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
// 邻接表,记录每门课程的依赖路径
List<List<Integer>> adjacency = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
adjacency.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] cp : prerequisites) {
adjacency.get(cp[1]).add(cp[0]);
}
// 标记节点
int[] flags = new int[numCourses];
// 依次判断每门课程的依赖路径是否存在环
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (!dfs(adjacency, flags, i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean dfs(List<List<Integer>> adjacency, int[] flags, int i) {
if (flags[i] == 1) {
return false;
}
if (flags[i] == -1) {
return true;
}
// flag=1表示该节点(课程)已经在依赖路径上,如果后面有节点又指向该节点,说明存在环,返回false
flags[i] = 1;
// 深度遍历依赖课程
for (Integer j : adjacency.get(i)) {
if (!dfs(adjacency, flags, j)) {
return false;
}
}
flags[i] = -1;
return true;
}
}
二分搜索与二叉排序树
labuladong-我写了首诗,让你闭着眼睛也能写对二分搜索
二分查找框架:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
int binarySearch(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = ...;
while(...) {
// 防止 left 和 right 太大直接相加导致溢出
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
...
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = ...
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = ...
}
}
return ...;
}
不要出现 else,而是把所有情况用 else if 写清楚,这样可以清楚地展现所有细节。
35.搜索插入位置【简单】【数组、二分查找】
给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
你可以假设数组中无重复元素。
题解1-用「排除法」(减治思想)写二分查找问题、与其它二分查找模板的比较
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class SearchInsertPosition {
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int len = nums.length;
int left = 0;
// 因为有可能数组的最后一个元素的位置的下一个是我们要找的,故右边界是 len
int right = len;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return left;
}
}
34.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置【中等】【数组、二分查找】
给定一个按照升序排列的整数数组 nums,和一个目标值 target。找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。
你的算法时间复杂度必须是 O(log n) 级别。
如果数组中不存在目标值,返回 [-1, -1]。
题解2-labuladong-我写了首诗,让你闭着眼睛也能写对二分搜索
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
class FindFirstAndLastPositionOfElementInSortedArray {
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
left = mid;
right = mid;
// 搜索左右边界
while (left - 1 >= 0 && nums[left - 1] == target) {
left--;
}
while (right + 1 < nums.length && nums[right + 1] == target) {
right++;
}
break;
}
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
int[] res;
if (nums[left] != target) {
res = new int[]{-1, -1};
} else {
res = new int[]{left, right};
}
return res;
}
}
33.搜索旋转排序数组【中等】【数组、二分查找】
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。搜索一个给定的目标值,如果数组中存在这个目标值,则返回它的索引,否则返回 -1 。
你可以假设数组中不存在重复的元素。你的算法时间复杂度必须是 O(log n) 级别。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class SearchInRotatedSortedArray {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
if (nums[0] <= nums[mid]) {
if (nums[0] <= target && target < nums[mid]) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
} else {
if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[nums.length - 1]) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
297.二叉树的序列化与反序列化【困难】【树、设计】
序列化是将一个数据结构或者对象转换为连续的比特位的操作,进而可以将转换后的数据存储在一个文件或者内存中,同时也可以通过网络传输到另一个计算机环境,采取相反方式重构得到原数据。
请设计一个算法来实现二叉树的序列化与反序列化。这里不限定你的序列 / 反序列化算法执行逻辑,你只需要保证一个二叉树可以被序列化为一个字符串并且将这个字符串反序列化为原始的树结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
public class SerializeAndDeserializeBinaryTree {
public void rserialize(TreeNode root, StringBuilder str) {
if (root == null) {
str.append("Null,");
} else {
str.append(root.val).append(",");
rserialize(root.left, str);
rserialize(root.right, str);
}
}
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder strRes = new StringBuilder();
rserialize(root, strRes);
return strRes.toString();
}
public TreeNode rdeserialize(List<String> list) {
if ("Null".equals(list.get(0))) {
list.remove(0);
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(list.get(0)));
list.remove(0);
root.left = rdeserialize(list);
root.right = rdeserialize(list);
return root;
}
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] dataArray = data.split(",");
List<String> dataList = new LinkedList<>(Arrays.asList(dataArray));
return rdeserialize(dataList);
}
}
哈希表与字符串
5.最长回文子串【中等】【字符串、动态规划】
给定一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。你可以假设 s 的最大长度为 1000。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
class LongestPalindromicSubstring {
/**
* 中心扩散
*/
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() < 1) {
return "";
}
int start = 0, end = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int len1 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i);
int len2 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1);
int len = Math.max(len1, len2);
if (len > end - start) {
start = i - (len - 1) / 2;
end = i + len / 2;
}
}
return s.substring(start, end + 1);
}
private int expandAroundCenter(String s, int left, int right) {
// left = right 的时候,此时回文中心是一个字符,回文串的长度是奇数
// right = left + 1 的时候,此时回文中心是一个空隙,回文串的长度是偶数
int L = left, R = right;
while (L >= 0 && R < s.length() && s.charAt(L) == s.charAt(R)) {
L--;
R++;
}
return R - L - 1;
}
/**
* 动态规划:
* dp[i][j]表示字符串s[i...j]是否为回文串
* 状态转移方程:dp[i][j] = (s[i]==s[j]) and dp[i+1][j-1]
* 边界条件:j-1 - (i+1) + 1 < 2,整理得:j-i < 3
* 初始化,单个字符是回文串:dp[i][i] = true
*/
public String longestPalindrome1(String s) {
int len = s.length();
if (len < 2) {
return s;
}
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][i] = true;
}
int maxLen = 1;
int begin = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < len; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
dp[i][j] = false;
}
// 边界条件
else if (j - i < 3) {
dp[i][j] = true;
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1];
}
// 如果是回文串并且更长,更新长度和起始位置
if (dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > maxLen) {
maxLen = j - i + 1;
begin = i;
}
}
}
return s.substring(begin, begin + maxLen);
}
}
290.单词规律【简单】【哈希表】
给定一种规律 pattern 和一个字符串 str ,判断 str 是否遵循相同的规律。
这里的 遵循 指完全匹配,例如, pattern 里的每个字母和字符串 str 中的每个非空单词之间存在着双向连接的对应规律。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
class WordPattern {
public boolean wordPattern(String pattern, String str) {
Map<Character, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
String[] array = str.split(" ");
if (pattern.length() != array.length) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length(); i++) {
char patternI = pattern.charAt(i);
if (hashMap.containsKey(patternI)) {
if (!hashMap.get(patternI).equals(array[i])) {
return false;
}
} else {
if (hashMap.containsValue(array[i])) {
return false;
}
hashMap.put(patternI, array[i]);
}
}
return true;
}
}
49.字母异位词分组【中等】【哈希表、字符串】
给定一个字符串数组,将字母异位词组合在一起。字母异位词指字母相同,但排列不同的字符串。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
class GroupAnagrams {
/**
* 统计每个字符的次数作为key
*/
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
HashMap<String, List<String>> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : strs) {
// 统计26个字母次数作为key
int[] num = new int[26];
for (int j = 0; j < str.length(); j++) {
num[str.charAt(j) - 'a']++;
}
StringBuilder sKey = new StringBuilder();
for (int i : num) {
sKey.append(i);
}
String key = sKey.toString();
if (hashMap.containsKey(key)) {
hashMap.get(key).add(str);
} else {
hashMap.put(key, new LinkedList<>(Collections.singleton(str)));
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(hashMap.values());
}
/**
* 把每个字符串都映射到一个正数上。
* 算术基本定理,又称为正整数的唯一分解定理,即:
* 每个大于1的自然数,要么本身就是质数,要么可以写为2个以上的质数的积,而且这些质因子按大小排列之后,写法仅有一种方式。
*/
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams2(String[] strs) {
HashMap<Integer, List<String>> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
// 每个字母对应一个质数
int[] prime = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103};
for (String str : strs) {
int key = 1;
// 累乘得到 key
for (int j = 0; j < str.length(); j++) {
key *= prime[str.charAt(j) - 'a'];
}
if (hashMap.containsKey(key)) {
hashMap.get(key).add(str);
} else {
hashMap.put(key, new LinkedList<>(Collections.singleton(str)));
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(hashMap.values());
}
}
3.无重复字符的最长子串【中等】【哈希表、双指针、字符串、SlidingWindow】
给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
class LongestSubstringWithoutRepeatingCharacters {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int start = 0, maxLen = 0;
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
Character key = s.charAt(i);
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
start = Math.max(map.get(key) + 1, start);
}
map.put(key, i);
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, i - start + 1);
}
return maxLen;
}
}
187.重复的DNA序列【中等】【位运算、哈希表】
所有 DNA 都由一系列缩写为 A,C,G 和 T 的核苷酸组成,例如:“ACGAATTCCG”。在研究 DNA 时,识别 DNA 中的重复序列有时会对研究非常有帮助。
编写一个函数来查找目标子串,目标子串的长度为 10,且在 DNA 字符串 s 中出现次数超过一次。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
class RepeatedDnaSequences {
/**
* HashSet
*/
public List<String> findRepeatedDnaSequences(String s) {
HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
HashSet<String> res = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= s.length() - 10; i++) {
String key = s.substring(i, i + 10);
if (hashSet.contains(key)) {
res.add(key);
} else {
hashSet.add(key);
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(res);
}
/**
* 位运算
* 二进制映射map:A -> 00, C -> 01, G -> 10, T -> 11
* 用int存储,一般情况下是32位的,只有10个字母,每个字母对应两位,所以只需要 20 位,
* 把key和 11111111111111111111(0xfffff) 进行按位与,只保留低 20 位,
* 所以更新 key 的话需要三个步骤,左移两位 -> 加上当前的字母 -> 按位与操作。
* <p>
* 更新策略:
* 不用map,字母本质上就是一个数字,至于对应关系就是 ASCII 码值。
* A -> 65 1000001
* C -> 65 1000011
* G -> 65 1000111
* T -> 65 1010100
* 只用低三位就可以区分这四个字母了。
* 每次移3位,因为每个字母对应三位,10个字母总共需要30位,所以把key和(0x3fffffff)也就是30个1进行按位与。
*/
public List<String> findRepeatedDnaSequences2(String s) {
if (s.length() < 10) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
Set<String> res = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
int key = 0;
char[] array = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
key <<= 3;
key |= (array[i] & 7);
}
set.add(key);
for (int i = 10; i < s.length(); i++) {
key <<= 3;
key |= (array[i] & 7);
key &= 0x3fffffff;
if (set.contains(key)) {
res.add(s.substring(i - 9, i + 1));
} else {
set.add(key);
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(res);
}
}
76.最小覆盖子串【困难】【哈希表、双指针、字符串、SlidingWindow】
给你一个字符串 S、一个字符串 T,请在字符串 S 里面找出:包含 T 所有字符的最小子串。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
class MinimumWindowSubstring {
Map<Character, Integer> HashT = new HashMap<>();
Map<Character, Integer> HashS = new HashMap<>();
public boolean check() {
Iterator iter = HashT.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next();
Character key = (Character) entry.getKey();
Integer val = (Integer) entry.getValue();
if (HashS.getOrDefault(key, 0) < val) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
HashT.put(t.charAt(i), HashT.getOrDefault(t.charAt(i), 0) + 1);
}
int start = -1, end = -1, minLen = s.length() + 1;
int l = 0, r = -1;
while (r < s.length()) {
++r;
if (r < s.length() && HashT.containsKey(s.charAt(r))) {
HashS.put(s.charAt(r), HashS.getOrDefault(s.charAt(r), 0) + 1);
}
// 移动左边界
while (check() && l <= r) {
if (r - l + 1 < minLen) {
minLen = r - l + 1;
start = l;
end = l + minLen;
}
if (HashT.containsKey(s.charAt(l))) {
HashS.put(s.charAt(l), HashS.getOrDefault(s.charAt(l), 0) - 1);
}
++l;
}
}
return start == -1 ? "" : s.substring(start, end);
}
}
搜索
200.岛屿数量【中等】【深度优先搜索、宽度优先搜索、并查集】
给你一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
题解2-DFS + BFS + 并查集(Python 代码、Java 代码)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
class NumberOfIslands {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int num = 0;
int h = grid.length;
int w = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[h][w];
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1' && !visited[i][j]) {
num++;
visited[i][j] = true;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(i * w + j);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 当前位置
int cur = queue.poll();
int row = cur / w;
int col = cur % w;
// 当前位置4个方向遍历
if (row - 1 >= 0 && grid[row - 1][col] == '1' && !visited[row - 1][col]) {
queue.add((row - 1) * w + col);
visited[row - 1][col] = true;
}
if (row + 1 < h && grid[row + 1][col] == '1' && !visited[row + 1][col]) {
queue.add((row + 1) * w + col);
visited[row + 1][col] = true;
}
if (col - 1 >= 0 && grid[row][col - 1] == '1' && !visited[row][col - 1]) {
queue.add(row * w + col - 1);
visited[row][col - 1] = true;
}
if (col + 1 < w && grid[row][col + 1] == '1' && !visited[row][col + 1]) {
queue.add(row * w + col + 1);
visited[row][col + 1] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
return num;
}
}
127.单词接龙【中等】【广度优先搜索】
给定两个单词(beginWord 和 endWord)和一个字典,找到从 beginWord 到 endWord 的最短转换序列的长度。转换需遵循如下规则:
每次转换只能改变一个字母。 转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典中的单词。 说明:
如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。 所有单词具有相同的长度。 所有单词只由小写字母组成。 字典中不存在重复的单词。 你可以假设 beginWord 和 endWord 是非空的,且二者不相同。
题解2-广度优先遍历、双向广度优先遍历(Java、Python)
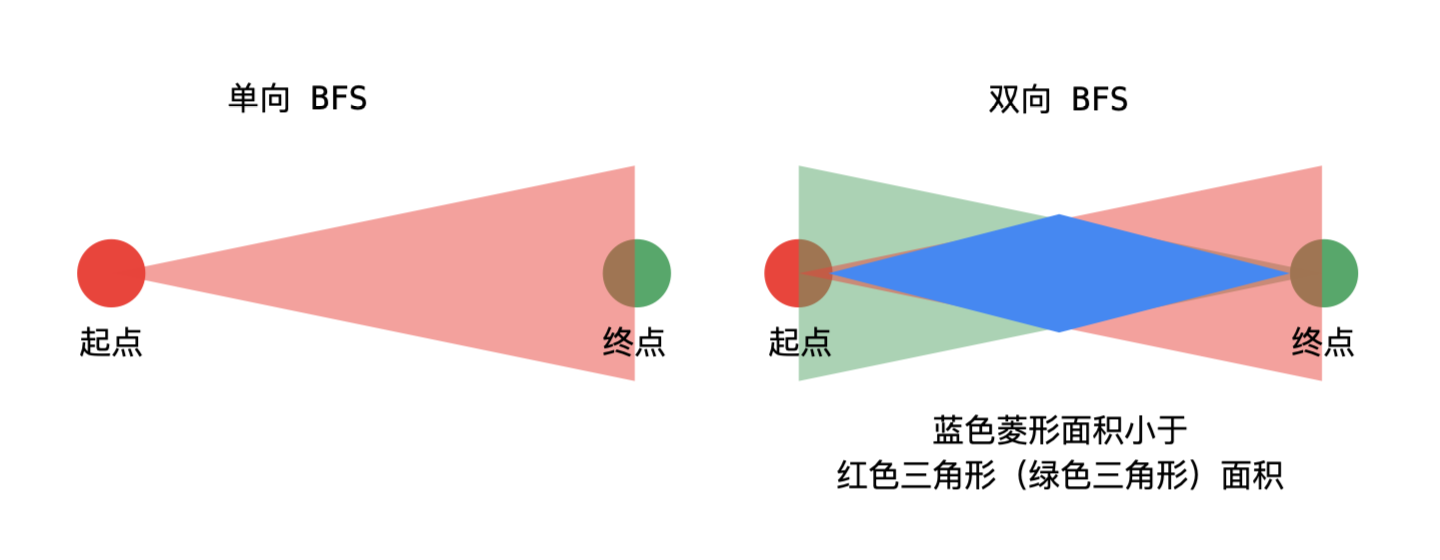
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
class WordLadder {
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
// 先将 wordList 放到哈希表里,便于判断某个单词是否在 wordList 里
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordList);
if (wordSet.size() == 0 || !wordSet.contains(endWord)) {
return 0;
}
wordSet.remove(beginWord);
// 图的广度优先遍历,必须使用的队列和表示是否访问过的 visited (数组,哈希表)
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(beginWord);
Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
visited.add(beginWord);
int wordLen = beginWord.length();
// 包含起点,因此初始化的时候步数为 1
int step = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int currentSize = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
// 依次遍历当前队列中的单词
String word = queue.poll();
char[] charArray = word.toCharArray();
// 修改每一个字符
for (int j = 0; j < wordLen; j++) {
char originChar = charArray[j];
for (char k = 'a'; k <= 'z'; k++) {
if (k == originChar) {
continue;
}
charArray[j] = k;
String nextWord = String.valueOf(charArray);
if (wordSet.contains(nextWord)) {
if (nextWord.equals(endWord)) {
return step + 1;
}
if (!visited.contains(nextWord)) {
queue.add(nextWord);
// 添加到队列以后,马上标记为已经访问
visited.add(nextWord);
}
}
}
// 恢复
charArray[j] = originChar;
}
}
step++;
}
return 0;
}
public int ladderLength2(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordList);
if (wordList.size() == 0 || !wordSet.contains(endWord)) {
return 0;
}
Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
// 分别用左边和右边扩散的哈希表代替单向 BFS 里的队列
Set<String> beginVisited = new HashSet<>();
beginVisited.add(beginWord);
Set<String> endVisited = new HashSet<>();
endVisited.add(endWord);
int wordLen = beginWord.length();
int step = 1;
while (!beginVisited.isEmpty() && !endVisited.isEmpty()) {
// 优先选择小的哈希表进行扩散,考虑到的情况更少
if (beginVisited.size() > endVisited.size()) {
Set<String> tmp = beginVisited;
beginVisited = endVisited;
endVisited = tmp;
}
// nextLevelVisited 在扩散完成以后,会成为新的 beginVisited
Set<String> nextLevelVisited = new HashSet<>();
for (String word : beginVisited) {
char[] charArray = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < wordLen; i++) {
char originChar = charArray[i];
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
if (originChar == c) {
continue;
}
charArray[i] = c;
String nextWord = String.valueOf(charArray);
if (wordSet.contains(nextWord)) {
if (endVisited.contains(nextWord)) {
return step + 1;
}
if (!visited.contains(nextWord)) {
nextLevelVisited.add(nextWord);
visited.add(nextWord);
}
}
}
charArray[i] = originChar;
}
}
// 从 begin 这一侧向外扩散了一层
beginVisited = nextLevelVisited;
step++;
}
return 0;
}
}
126.单词接龙2【困难】【广度优先搜索、数组、字符串、回溯算法】
给定两个单词(beginWord 和 endWord)和一个字典 wordList,找出所有从 beginWord 到 endWord 的最短转换序列。转换需遵循如下规则:
每次转换只能改变一个字母。 转换后得到的单词必须是字典中的单词。 说明:
如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回一个空列表。 所有单词具有相同的长度。 所有单词只由小写字母组成。 字典中不存在重复的单词。 你可以假设 beginWord 和 endWord 是非空的,且二者不相同。
题解3-单双向广度优先遍历 + 回溯算法(Java、Python)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
class WordLadder2 {
private ArrayList<String> getNeighbors(String node, Set<String> dict) {
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<String>();
char chs[] = node.toCharArray();
for (char ch = 'a'; ch <= 'z'; ch++) {
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
if (chs[i] == ch) {
continue;
}
char old_ch = chs[i];
chs[i] = ch;
if (dict.contains(String.valueOf(chs))) {
res.add(String.valueOf(chs));
}
chs[i] = old_ch;
}
}
return res;
}
public List<List<String>> findLadders(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
List<List<String>> res = new LinkedList<>();
// 先将 wordList 放到哈希表里,便于判断某个单词是否在 wordList 里
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordList);
if (wordSet.size() == 0 || !wordSet.contains(endWord)) {
return res;
}
wordSet.remove(beginWord);
// 队列和已访问节点
Queue<List<String>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<String> path = new LinkedList<>();
path.add(beginWord);
queue.offer(path);
Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
visited.add(beginWord);
boolean isFound = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int currentSize = queue.size();
Set<String> subVisited = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
List<String> p = queue.poll();
// 得到当前路径的末尾单词
String temp = p.get(p.size() - 1);
// 一次性得到所有的下一个节点
ArrayList<String> neighbors = getNeighbors(temp, wordSet);
for (String nextWord : neighbors) {
// 只考虑之前没有出现过的单词
if (!visited.contains(nextWord)) {
// 到达结束单词
if (nextWord.equals(endWord)) {
isFound = true;
p.add(nextWord);
res.add(new ArrayList<>(p));
p.remove(p.size() - 1);
}
// 加入当前单词
p.add(nextWord);
queue.offer(new ArrayList<String>(p));
p.remove(p.size() - 1);
subVisited.add(nextWord);
}
}
}
visited.addAll(subVisited);
if (isFound) {
break;
}
}
return res;
}
}
473.火柴拼正方形【中等】【深度优先搜索】
还记得童话《卖火柴的小女孩》吗?现在,你知道小女孩有多少根火柴,请找出一种能使用所有火柴拼成一个正方形的方法。不能折断火柴,可以把火柴连接起来,并且每根火柴都要用到。
输入为小女孩拥有火柴的数目,每根火柴用其长度表示。输出即为是否能用所有的火柴拼成正方形。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
class MatchsticksToSquare {
/**
* @param squareSide 边长
* @param index 索引
* @param numsList 火柴数组
* @param sums 正方形各边长和
* @return 是否能拼成正方形
*/
public boolean dfs(int squareSide, int index, List<Integer> numsList, int[] sums) {
// 刚好用完火柴且四边相等则返回true
if (index == numsList.size()) {
return sums[0] == sums[1] && sums[1] == sums[2] && sums[2] == sums[3];
}
// 记录当前火柴长度
int element = numsList.get(index);
// 四边能否加上当前火柴
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
// 该边加上当前火柴长度不超过期望边长才进行尝试添加(排序功能在此起到剪枝作用)
if (sums[i] + element <= squareSide) {
sums[i] += element;
// 该边加上当前火柴长度后进行深度搜索
if (dfs(squareSide, index + 1, numsList, sums)) {
return true;
}
sums[i] -= element;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean makesquare(int[] nums) {
int[] sums = new int[4];
if (nums == null || nums.length < 4) {
return false;
}
// 周长
int perimeter = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
perimeter += num;
}
// 边长
int squareSide = perimeter / 4;
if (squareSide * 4 != perimeter) {
return false;
}
// 排序,从大到小排序,长的边如果超过某边还需要的长度,就直接跳过了(相当于剪枝)
List<Integer> numsList = Arrays.stream(nums).boxed().sorted(Collections.reverseOrder()).collect(Collectors.toList());
return this.dfs(squareSide, 0, numsList, sums);
}
}
407.接雨水2【困难】【堆、广度优先搜索】
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵,其中的值均为非负整数,代表二维高度图每个单元的高度,请计算图中形状最多能接多少体积的雨水。
1
动态规划
70.爬楼梯【简单】【动态规划】
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
注意:给定 n 是一个正整数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class ClimbingStairs {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n < 2) {
return 1;
}
int res = 0;
int dp0 = 1;
int dp1 = 1;
n = n - 1;
while (n-- > 0) {
res = dp0 + dp1;
dp0 = dp1;
dp1 = res;
}
return res;
}
}
198.打家劫舍【简单】【动态规划】
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你 不触动警报装置的情况下 ,一夜之内能够偷窃到的最高金额。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class HouseRobber {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int len = nums.length;
if (len == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
int dp1 = nums[0];
int dp2 = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < len; i++) {
int tmp = dp2;
dp2 = Math.max(dp1 + nums[i], dp2);
dp1 = tmp;
}
return dp2;
}
}
53.最大子序和【简单】【数组、分治算法、动态规划】
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class MaximumSubarray {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int res = nums[0];
int sum = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
sum = Math.max(sum + num, num);
res = Math.max(res, sum);
}
return res;
}
}
322.零钱兑换【中等】【动态规划】
给定不同面额的硬币 coins 和一个总金额 amount。编写一个函数来计算可以凑成总金额所需的最少的硬币个数。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1。
题解2-动态规划、使用「完全背包」问题思路、图的广度优先遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
public class CoinChange {
/**
* 动态规划
*/
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
// dp[i]意义:组成金额 i 所需最少的硬币数量
// 状态转移方程:dp[i] = min( dp[i-coin] + 1 for coin in coins),coin<i
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < amount + 1; i++) {
dp[i] = amount + 1;
}
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= amount; i++) {
for (int coin : coins) {
if (coin <= i) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coin] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
/**
* 广度优先遍历,最短路径问题
*/
public int coinChange2(int[] coins, int amount) {
if (amount == 0) {
return 0;
}
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[amount + 1];
visited[amount] = true;
queue.offer(amount);
// 从小到大排序,排序是为了剪枝
Arrays.sort(coins);
int step = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
// 遍历当前层
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int head = queue.poll();
for (int coin : coins) {
int next = head - coin;
// 找到了一个最短路径
if (next == 0) {
return step;
}
// 硬币大于总额,排序剪枝
if (next < 0) {
break;
}
if (!visited[next]) {
queue.offer(next);
visited[next] = true;
}
}
}
step++;
}
return -1;
}
}
120.三角形最小路径和【中等】【数组、动态规划】
给定一个三角形,找出自顶向下的最小路径和。每一步只能移动到下一行中相邻的结点上。
相邻的结点 在这里指的是 下标 与 上一层结点下标 相同或者等于 上一层结点下标 + 1 的两个结点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Triangle {
public int minimumTotal(List<List<Integer>> triangle) {
int len = triangle.size();
int[] dp = new int[len + 1];
// 从最后一行往前
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j + 1]) + triangle.get(i).get(j);
}
}
return dp[0];
}
}
300.最长上升子序列【中等】【二分查找、动态规划】
给定一个无序的整数数组,找到其中最长上升子序列的长度。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
class LongestIncreasingSubsequence {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length < 2) {
return nums.length;
}
// dp[i] 代表含第 i 个元素的最长上升子序列的长度。
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[j] < nums[i]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], 1 + dp[j]);
}
}
}
int res = dp[0];
for (int value : dp) {
res = Math.max(res, value);
}
return res;
}
public int lengthOfLIS2(int[] nums) {
// tails[k] 的值代表 长度为 k+1 的子序列尾部元素的值
int[] tails = new int[nums.length];
int res = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
// 二分法找到位置
int left = 0, right = res;
while (left < right) {
int m = (left + right) / 2;
if (tails[m] < num) {
left = m + 1;
} else {
right = m;
}
}
tails[left] = num;
if (res == right) {
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
}
64.最小路径和【中等】【数组、动态规划】
给定一个包含非负整数的 m x n 网格,请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小。
说明:每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class MinimumPathSum {
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) {
continue;
} else if (i == 0) {
grid[i][j] = grid[i][j - 1] + grid[i][j];
} else if (j == 0) {
grid[i][j] = grid[i - 1][j] + grid[i][j];
} else {
grid[i][j] = Math.min(grid[i - 1][j], grid[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j];
}
}
}
return grid[grid.length - 1][grid[0].length - 1];
}
}
174.地下城游戏【困难】【二分查找、动态规划】
一些恶魔抓住了公主(P)并将她关在了地下城的右下角。地下城是由 M x N 个房间组成的二维网格。我们英勇的骑士(K)最初被安置在左上角的房间里,他必须穿过地下城并通过对抗恶魔来拯救公主。
骑士的初始健康点数为一个正整数。如果他的健康点数在某一时刻降至 0 或以下,他会立即死亡。
有些房间由恶魔守卫,因此骑士在进入这些房间时会失去健康点数(若房间里的值为负整数,则表示骑士将损失健康点数);其他房间要么是空的(房间里的值为 0),要么包含增加骑士健康点数的魔法球(若房间里的值为正整数,则表示骑士将增加健康点数)。
为了尽快到达公主,骑士决定每次只向右或向下移动一步。
编写一个函数来计算确保骑士能够拯救到公主所需的最低初始健康点数。
例如,考虑到如下布局的地下城,如果骑士遵循最佳路径 右 -> 右 -> 下 -> 下,则骑士的初始健康点数至少为 7。
-2 (K) -3 3 -5 -10 1 10 30 -5 (P)
说明:
骑士的健康点数没有上限。
任何房间都可能对骑士的健康点数造成威胁,也可能增加骑士的健康点数,包括骑士进入的左上角房间以及公主被监禁的右下角房间。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
class DungeonGame {
public int calculateMinimumHP(int[][] dungeon) {
int m = dungeon.length, n = dungeon[0].length;
// dp[i][j] 表示从坐标 (i,j) 到终点所需的最小初始值健康点
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dp[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
// 右下角向右、向下延长一个,减少边界条件判断,到达终点必须大于0,最小为1
dp[m][n - 1] = dp[m - 1][n] = 1;
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
// 判断向下、向右需要最少健康点
int minn = Math.min(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j + 1]);
// 健康点数在某一时刻降至 0 或以下,会立即死亡,所以最小为1
dp[i][j] = Math.max(minn - dungeon[i][j], 1);
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
}
高级数据结构
trie树(字典树)、并查集、线段树。
208.实现trie(前缀树)【中等】【设计、字典树】
实现一个 Trie (前缀树),包含 insert, search, 和 startsWith 这三个操作。
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // 返回 true
trie.search("app"); // 返回 false
trie.startsWith("app"); // 返回 true
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // 返回 true
说明:
你可以假设所有的输入都是由小写字母 a-z 构成的。 保证所有输入均为非空字符串。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
class Trie {
private class TrieNode {
private boolean isEnd;
private TrieNode[] next;
public TrieNode() {
isEnd = false;
// 每个节点最多有26个不同的小写字母
next = new TrieNode[26];
}
}
TrieNode root;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
/**
* Inserts a word into the trie.
*/
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int ch = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (cur.next[ch] == null) {
cur.next[ch] = new TrieNode();
}
cur = cur.next[ch];
}
// 加上end标记,表示为一个单词
cur.isEnd = true;
}
/**
* Returns if the word is in the trie.
*/
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int ch = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (cur.next[ch] == null) {
return false;
}
cur = cur.next[ch];
}
// 此处是否为单词
return cur.isEnd;
}
/**
* Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix.
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
int ch = prefix.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (cur.next[ch] == null) {
return false;
}
cur = cur.next[ch];
}
// 直接返回true
return true;
}
}
211.添加与搜索单词-数据结构设计【中等】【设计、字典树、回溯算法】
设计一个支持以下两种操作的数据结构:
1
2
void addWord(word)
bool search(word)
search(word) 可以搜索文字或正则表达式字符串,字符串只包含字母 . 或 a-z 。 . 可以表示任何一个字母。
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
addWord("bad")
addWord("dad")
addWord("mad")
search("pad") -> false
search("bad") -> true
search(".ad") -> true
search("b..") -> true
说明:
你可以假设所有单词都是由小写字母 a-z 组成的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
class WordDictionary {
private static class TrieNode {
private boolean isEnd;
private final TrieNode[] next;
public TrieNode() {
isEnd = false;
// 每个节点最多有26个不同的小写字母
next = new TrieNode[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
next[i] = null;
}
}
}
TrieNode root;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public WordDictionary() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
/**
* Adds a word into the data structure.
*/
public void addWord(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int ch = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (cur.next[ch] == null) {
cur.next[ch] = new TrieNode();
}
cur = cur.next[ch];
}
// 加上end标记,表示为一个单词
cur.isEnd = true;
}
/**
* Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter.
*/
public boolean search(String word) {
return searchHelp(word, root);
}
private boolean searchHelp(String word, TrieNode root) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
// 对于 . , 递归判断所有不为空的孩子
if (word.charAt(i) == '.') {
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
if (cur.next[j] != null) {
if (searchHelp(word.substring(i + 1), cur.next[j])) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// 其他字母
int ch = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (cur.next[ch] == null) {
return false;
}
cur = cur.next[ch];
}
// 此处是否为单词
return cur.isEnd;
}
}
547.朋友圈【中等】【深度优先搜索、并查集】
班上有 N 名学生。其中有些人是朋友,有些则不是。他们的友谊具有是传递性。如果已知 A 是 B 的朋友,B 是 C 的朋友,那么我们可以认为 A 也是 C 的朋友。所谓的朋友圈,是指所有朋友的集合。
给定一个 N * N 的矩阵 M,表示班级中学生之间的朋友关系。如果M[i][j] = 1,表示已知第 i 个和 j 个学生互为朋友关系,否则为不知道。你必须输出所有学生中的已知的朋友圈总数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
class FriendCircles {
/**
* DFS
*/
public void dfs(int[][] M, int[] visited, int i) {
for (int j = 0; j < M.length; j++) {
if (M[i][j] == 1 && visited[j] == 0) {
visited[j] = 1;
dfs(M, visited, j);
}
}
}
public int findCircleNum(int[][] M) {
int[] visited = new int[M.length];
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < M.length; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
dfs(M, visited, i);
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
/**
* 并查集
*/
class UnionFind {
// 连通分量个数
private int count;
// 存储父节点
private final int[] parent;
// 记录树的“重量”
private final int[] size;
public UnionFind(int n) {
// 初始全部自己和自己连通
this.count = n;
parent = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 父节点指针初始指向自己
parent[i] = i;
// 重量初始全部为1
size[i] = 1;
}
}
// 返回某个节点 x 的根节点
private int find(int x) {
while (parent[x] != x) {
// 进行路径压缩
parent[x] = parent[parent[x]];
x = parent[x];
}
return x;
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
// 两个节点已经指向同一父节点
if (rootP == rootQ) {
return;
}
// 小树接到大树下面,较平衡
if (size[rootP] > size[rootQ]) {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
size[rootP] += size[rootQ];
} else {
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
size[rootQ] += size[rootP];
}
// 连通量减少一个
count--;
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
return rootP == rootQ;
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
}
public int findCircleNum2(int[][] M) {
int n = M.length;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (M[i][j] == 1) {
uf.union(i, j);
}
}
}
return uf.count();
}
}
303.区域和的检索【中等】【动态规划、线段树】
给定一个整数数组 nums,求出数组从索引 i 到 j (i ≤ j) 范围内元素的总和,包含 i, j 两点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
class NumArray {
// 前缀和
private final int[] sum;
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
// sum长度多一位
sum = new int[nums.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum[i + 1] = sum[i] + nums[i];
}
}
public int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return sum[j + 1] - sum[i];
}
}